Otoscope: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Ototskop_mit_Ohrtrichtern.jpg|Otoscope with ear funnels | |||
File:Otoscope_Spengler_SMARTLED_5500.png|Otoscope Spengler SMARTLED 5500 | |||
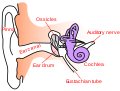
File:Ear-anatomy-text-small-en.svg|Diagram of ear anatomy | |||
File:Gray909.png|Anatomical illustration of the ear | |||
File:Performing_an_Otoscopic_exam.jpg|Performing an otoscopic exam | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:39, 18 February 2025
Otoscope
An otoscope or auriscope is a medical device which is used to look into the ears. Health care providers use otoscopes to screen for illness during regular check-ups and also to investigate ear symptoms. An otoscope potentially gives a view of the ear canal and tympanic membrane or eardrum.
Uses[edit]
Because the eardrum is the border separating the external ear canal from the middle ear, its characteristics can give the healthcare professional a lot of information about what's happening on the other side of the eardrum.
Types[edit]
There are two types of otoscopes: pocket otoscope and standard otoscope. The pocket otoscope has a handle that uses batteries to light the viewing instrument. The standard otoscope is larger, has a cord, and is plugged into a wall for power.
Components[edit]
The otoscope consists of a handle and a head. The head contains a light source and a simple low-power magnifying lens, typically around 8 diopters (3x).
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />
External links[edit]
- Otoscope.org - Information on otoscopes