Glabella: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
[[Category:Medical Terminology]] | [[Category:Medical Terminology]] | ||
{{dictionary-stub1}} | {{dictionary-stub1}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Glabella.PNG | |||
File:Gray1193.svg | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:51, 17 February 2025
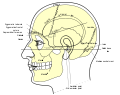
Glabella is the space between the eyebrows and above the nose. It is often used as a landmark in both anatomy and cosmetic surgery. The term is derived from the Latin word "glabellus", which means smooth.
Anatomy[edit]
The glabella is located on the frontal bone of the human skull and is the area between the supraorbital ridges/eyebrows. It is slightly depressed compared to the surrounding bones.
Clinical significance[edit]
In the field of medicine, the glabella is of interest for several reasons. It is often used as a landmark in craniofacial surgery. In addition, the glabella reflex is a clinical sign that can be used to assess the status of the frontal lobes and facial nerves.
Glabella reflex[edit]
The glabella reflex, also known as the Myerson's sign, is a primitive reflex. It is elicited by repetitive tapping on the glabella. The normal response is for the patient to blink with the first few taps, and then stop blinking. If the patient continues to blink with every tap, it is considered a positive Myerson's sign, which can be indicative of Parkinson's disease or other neurological disorders.
Cosmetic surgery[edit]
In cosmetic surgery, the glabella is often a target for botox injections to reduce the appearance of frown lines. It is also a common site for the injection of dermal fillers to smooth out the skin and reduce the appearance of wrinkles.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />