Motor cortex: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 53: | Line 53: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
{{dictionary-stub1}} | {{dictionary-stub1}} | ||
== Motor_cortex == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Human_motor_cortex.jpg|Human motor cortex | |||
File:Figure_35_03_04.jpg|Figure 35 03 04 | |||
File:Motor_Cortex_monkey.jpg|Motor Cortex monkey | |||
File:Human_motor_map.jpg|Human motor map | |||
File:M1_microcircuit_model.jpg|M1 microcircuit model | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 21:26, 23 February 2025
Motor Cortex
The Motor Cortex is a region of the cerebral cortex involved in the planning, control, and execution of voluntary movements. It is located in the posterior part of the frontal lobe.
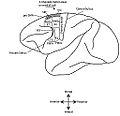
Anatomy[edit]
The motor cortex can be divided into three areas:
1. The primary motor cortex (M1) 2. The premotor cortex (PMC) 3. The supplementary motor area (SMA)
Each of these areas plays a unique role in motor function.
Primary Motor Cortex[edit]
The primary motor cortex, or M1, is located in the precentral gyrus, and is the main contributor to generating neural impulses that pass down to the spinal cord and control the execution of movement.
Premotor Cortex[edit]
The premotor cortex, or PMC, is involved in planning and executing movements. It is located anterior to the primary motor cortex.
Supplementary Motor Area[edit]
The supplementary motor area, or SMA, is involved in the planning and coordination of complex movements. It is located on the midline surface of the hemisphere, anterior to the primary motor cortex.
Function[edit]
The motor cortex is involved in the planning, control, and execution of voluntary movements. More specifically, the primary motor cortex is responsible for the direct control of voluntary movement, while the premotor and supplementary motor areas are involved in the planning and coordination of movements.
Clinical Significance[edit]
Damage to the motor cortex can result in a variety of motor disorders, including paralysis, apraxia, and motor neurone disease. In addition, the motor cortex is often a target for neurorehabilitation following a stroke or brain injury.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />