Trichorrhexis nodosa: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
== | | name = Trichorrhexis nodosa | ||
| image = [[File:Tricho-hepato-enteric_syndrome_(1).jpg]] | |||
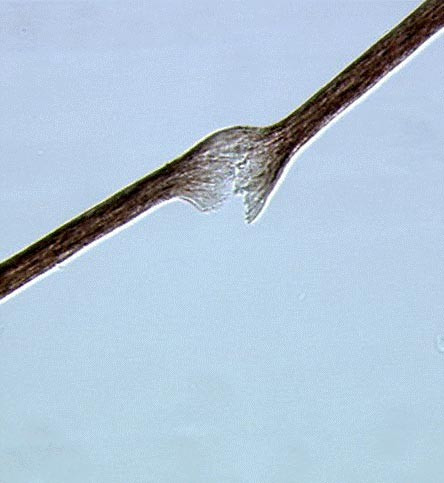
| caption = Trichorrhexis nodosa in a patient with tricho-hepato-enteric syndrome | |||
| synonyms = [[Knotted hair]] | |||
= | | field = [[Dermatology]] | ||
| symptoms = [[Hair breakage]], [[hair fragility]] | |||
| complications = [[Hair loss]] | |||
| onset = Childhood or adulthood | |||
== | | duration = Chronic | ||
| causes = [[Genetic disorder]], [[physical trauma]], [[chemical exposure]] | |||
| risks = [[Excessive hair styling]], [[chemical treatments]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Clinical examination]], [[trichoscopy]] | |||
== | | differential = [[Monilethrix]], [[pili torti]], [[trichothiodystrophy]] | ||
| treatment = [[Avoidance of trauma]], [[gentle hair care]], [[moisturizing treatments]] | |||
| prognosis = Good with proper care | |||
| frequency = Common | |||
== | }} | ||
{{Short description|A hair shaft disorder}} | |||
* [[ | '''Trichorrhexis nodosa''' is a condition that affects the hair shaft, leading to hair breakage and the appearance of white nodules along the hair strand. It is a common cause of hair fragility and can be either acquired or congenital. | ||
==Presentation== | |||
* [[ | Trichorrhexis nodosa is characterized by the presence of nodes or swellings along the hair shaft. These nodes are weak points where the hair is prone to breakage. The condition can affect any hair-bearing area of the body, but it is most commonly observed on the scalp. | ||
* [[ | ===Symptoms=== | ||
Individuals with trichorrhexis nodosa may notice: | |||
== References == | * Brittle hair that breaks easily | ||
* White nodules along the hair shaft | |||
* Hair that appears frizzy or lacks shine | |||
===Causes=== | |||
Trichorrhexis nodosa can be caused by: | |||
* [[Physical trauma]] to the hair, such as excessive brushing or styling | |||
* Chemical damage from hair treatments like bleaching or perming | |||
* Genetic factors, in the case of congenital trichorrhexis nodosa | |||
==Diagnosis== | |||
Diagnosis of trichorrhexis nodosa is typically made through clinical examination and microscopic analysis of the hair. Under a microscope, the hair shaft will show characteristic nodes and fractures. | |||
==Management== | |||
Management of trichorrhexis nodosa involves addressing the underlying cause and minimizing further damage to the hair. Recommendations may include: | |||
* Reducing physical and chemical trauma to the hair | |||
* Using gentle hair care products | |||
* Ensuring adequate nutrition to support hair health | |||
==Related conditions== | |||
Trichorrhexis nodosa can be associated with other conditions, such as: | |||
* [[Tricho-hepato-enteric syndrome]] | |||
==See also== | |||
* [[Hair shaft disorders]] | |||
* [[Hair care]] | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist}} | |||
==External links== | |||
* [https://www.dermnetnz.org/topics/trichorrhexis-nodosa DermNet NZ: Trichorrhexis Nodosa] | |||
[[Category:Hair diseases]] | |||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 23:20, 6 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Trichorrhexis nodosa | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Knotted hair |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Hair breakage, hair fragility |
| Complications | Hair loss |
| Onset | Childhood or adulthood |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetic disorder, physical trauma, chemical exposure |
| Risks | Excessive hair styling, chemical treatments |
| Diagnosis | Clinical examination, trichoscopy |
| Differential diagnosis | Monilethrix, pili torti, trichothiodystrophy |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Avoidance of trauma, gentle hair care, moisturizing treatments |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Good with proper care |
| Frequency | Common |
| Deaths | N/A |
A hair shaft disorder
Trichorrhexis nodosa is a condition that affects the hair shaft, leading to hair breakage and the appearance of white nodules along the hair strand. It is a common cause of hair fragility and can be either acquired or congenital.
Presentation[edit]
Trichorrhexis nodosa is characterized by the presence of nodes or swellings along the hair shaft. These nodes are weak points where the hair is prone to breakage. The condition can affect any hair-bearing area of the body, but it is most commonly observed on the scalp.
Symptoms[edit]
Individuals with trichorrhexis nodosa may notice:
- Brittle hair that breaks easily
- White nodules along the hair shaft
- Hair that appears frizzy or lacks shine
Causes[edit]
Trichorrhexis nodosa can be caused by:
- Physical trauma to the hair, such as excessive brushing or styling
- Chemical damage from hair treatments like bleaching or perming
- Genetic factors, in the case of congenital trichorrhexis nodosa
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of trichorrhexis nodosa is typically made through clinical examination and microscopic analysis of the hair. Under a microscope, the hair shaft will show characteristic nodes and fractures.
Management[edit]
Management of trichorrhexis nodosa involves addressing the underlying cause and minimizing further damage to the hair. Recommendations may include:
- Reducing physical and chemical trauma to the hair
- Using gentle hair care products
- Ensuring adequate nutrition to support hair health
Related conditions[edit]
Trichorrhexis nodosa can be associated with other conditions, such as:
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>


