Dacryon: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
[[Category:Radiology]] | [[Category:Radiology]] | ||
[[Category:Craniofacial surgery]] | [[Category:Craniofacial surgery]] | ||
== Dacryon == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Dacryon.PNG|Description of Dacryon.PNG | |||
File:Gray190.png|Description of Gray190.png | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:49, 17 February 2025
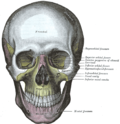
Dacryon is a term used in anatomy to refer to the point of junction between the frontal bone, maxilla, and the lacrimal bone in the human skull. It is a significant anatomical landmark, particularly in the field of craniofacial surgery and radiology.
Anatomy[edit]
The dacryon is located on the medial wall of the orbit, at the junction of the frontal process of the maxilla, the lacrimal bone, and the frontal bone. It is the anterior point of the frontonasal suture and the posterior point of the frontomaxillary suture. The dacryon is an important landmark in the paranasal sinuses and is often used as a reference point in radiological studies of the skull.
Clinical Significance[edit]
The location of the dacryon is significant in several surgical procedures involving the orbit and paranasal sinuses. It is often used as a reference point in endoscopic sinus surgery and craniofacial surgery. In addition, the dacryon is a critical landmark in the diagnosis and treatment of various conditions affecting the orbit and paranasal sinuses, including sinusitis, nasal polyps, and orbital cellulitis.
See Also[edit]
- Frontal bone
- Maxilla
- Lacrimal bone
- Orbit
- Paranasal sinuses
- Endoscopic sinus surgery
- Craniofacial surgery
References[edit]
<references />