Enclomifene: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Enclomifene == | |||
[[File:Enclomifene.png|thumb|right|Chemical structure of Enclomifene]] | |||
Enclomifene | |||
'''Enclomifene''' is a nonsteroidal [[selective estrogen receptor modulator]] (SERM) that is used primarily in the treatment of [[male hypogonadism]] and as a fertility agent. It is one of the two geometric isomers of [[clomifene]], the other being [[zuclomifene]]. | |||
Enclomifene is used | |||
== | == Mechanism of Action == | ||
Enclomifene acts by binding to estrogen receptors in the [[hypothalamus]], which leads to an increase in the release of [[gonadotropin-releasing hormone]] (GnRH). This, in turn, stimulates the [[pituitary gland]] to secrete [[luteinizing hormone]] (LH) and [[follicle-stimulating hormone]] (FSH), which promote the production of [[testosterone]] in the [[testes]]. | |||
Enclomifene | |||
== | == Clinical Uses == | ||
Enclomifene is primarily used in the treatment of male hypogonadism, a condition characterized by low levels of testosterone. It is also used as a fertility agent in men, as it can increase sperm production by stimulating the testes. | |||
=== Male Hypogonadism === | |||
In cases of male hypogonadism, enclomifene is used to restore normal testosterone levels. This can help alleviate symptoms such as fatigue, decreased libido, and loss of muscle mass. | |||
=== Fertility Treatment === | |||
Enclomifene is used to treat male infertility by increasing sperm count and motility. It is often prescribed when low sperm count is a contributing factor to infertility. | |||
== Side Effects == | |||
Common side effects of enclomifene include hot flashes, mood swings, and headaches. In some cases, it may cause visual disturbances or gastrointestinal discomfort. | |||
== Pharmacokinetics == | |||
Enclomifene is administered orally and is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. It undergoes hepatic metabolism and is excreted primarily in the feces. | |||
== Related Compounds == | |||
Enclomifene is closely related to [[clomifene]], which is a mixture of enclomifene and zuclomifene. Clomifene is also used as a fertility agent in women to induce ovulation. | |||
== Related Pages == | |||
* [[Clomifene]] | |||
* [[Selective estrogen receptor modulator]] | * [[Selective estrogen receptor modulator]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Male hypogonadism]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Testosterone]] | ||
[[Category:Selective estrogen receptor modulators]] | [[Category:Selective estrogen receptor modulators]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Andrology]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Infertility]] | ||
Latest revision as of 03:53, 13 February 2025
Enclomifene[edit]
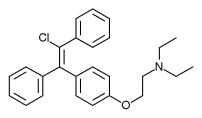
Enclomifene is a nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) that is used primarily in the treatment of male hypogonadism and as a fertility agent. It is one of the two geometric isomers of clomifene, the other being zuclomifene.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
Enclomifene acts by binding to estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus, which leads to an increase in the release of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). This, in turn, stimulates the pituitary gland to secrete luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which promote the production of testosterone in the testes.
Clinical Uses[edit]
Enclomifene is primarily used in the treatment of male hypogonadism, a condition characterized by low levels of testosterone. It is also used as a fertility agent in men, as it can increase sperm production by stimulating the testes.
Male Hypogonadism[edit]
In cases of male hypogonadism, enclomifene is used to restore normal testosterone levels. This can help alleviate symptoms such as fatigue, decreased libido, and loss of muscle mass.
Fertility Treatment[edit]
Enclomifene is used to treat male infertility by increasing sperm count and motility. It is often prescribed when low sperm count is a contributing factor to infertility.
Side Effects[edit]
Common side effects of enclomifene include hot flashes, mood swings, and headaches. In some cases, it may cause visual disturbances or gastrointestinal discomfort.
Pharmacokinetics[edit]
Enclomifene is administered orally and is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. It undergoes hepatic metabolism and is excreted primarily in the feces.
Related Compounds[edit]
Enclomifene is closely related to clomifene, which is a mixture of enclomifene and zuclomifene. Clomifene is also used as a fertility agent in women to induce ovulation.