Diclofenamide: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
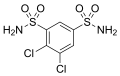
File:Diclofenamide.svg|Chemical structure of Diclofenamide | |||
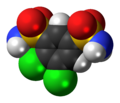
File:Diclofenamide-3D-spacefill.png|3D space-filling model of Diclofenamide | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:59, 17 February 2025
Diclofenamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor used to treat glaucoma and other conditions that involve fluid retention. It works by decreasing the amount of fluid that can build up in the eye. It also reduces the build-up of body fluids caused by congestive heart failure or certain medications.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
Diclofenamide works by inhibiting the enzyme carbonic anhydrase, which plays a key role in the production of aqueous humor in the eye. By inhibiting this enzyme, diclofenamide reduces the production of this fluid, thereby reducing intraocular pressure.
Uses[edit]
Diclofenamide is primarily used to treat glaucoma, a condition characterized by increased pressure within the eye. It can also be used to treat edema (fluid retention) due to congestive heart failure or certain medications.
Side Effects[edit]
Common side effects of diclofenamide include nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, and tiredness. More serious side effects can include kidney stones, anemia, and drowsiness.
Contraindications[edit]
Diclofenamide should not be used in patients with hypersensitivity to sulfonamides, severe kidney or liver disease, or adrenal gland dysfunction.
Interactions[edit]
Diclofenamide can interact with other medications, including aspirin, corticosteroids, and digitalis.
Dosage[edit]
The dosage of diclofenamide varies depending on the condition being treated and the patient's response to treatment.