Nucleus basalis: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
[[Category:Neuroscience]] | [[Category:Neuroscience]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
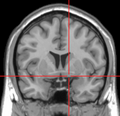
File:Substantia_innominata_MRI.PNG|Substantia innominata MRI | |||
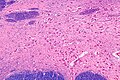
File:Nucleus_basalis_of_Meynert_-_intermed_mag.jpg|Nucleus basalis of Meynert - Intermediate Magnification | |||
File:Nucleus_basalis_of_Meynert_-_low_mag.jpg|Nucleus basalis of Meynert - Low Magnification | |||
File:Nucleus_basalis_of_Meynert_-l-_very_low_mag.jpg|Nucleus basalis of Meynert - Very Low Magnification | |||
File:Nucleus_basalis_of_Meynert_-_very_high_mag.jpg|Nucleus basalis of Meynert - Very High Magnification | |||
File:Cholinergic_neurons_of_the_nucleus_basalis_of_Meynert.jpg|Cholinergic neurons of the nucleus basalis of Meynert | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:32, 18 February 2025
Nucleus basalis is a group of neurons located in the basal forebrain. It is also known as the Basal nucleus of Meynert or Nucleus basalis of Meynert (NbM). This region of the brain is primarily associated with acetylcholine production and is implicated in several neurological disorders, including Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease.
Etymology[edit]
The nucleus basalis is named after Theodor Meynert, a German-Austrian psychiatrist and neuroanatomist, who first described this region of the brain in the 19th century. The term "nucleus" refers to a group of neurons in the central nervous system, while "basalis" indicates its location in the basal part of the brain.
Structure[edit]
The nucleus basalis is located in the substantia innominata of the basal forebrain. It is a collection of magnocellular neurons, which are large cells capable of producing and releasing the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. The nucleus basalis extends from the anterior commissure to the globus pallidus, and it is divided into several subregions, including the anterior, intermediate, and posterior sectors.
Function[edit]
The primary function of the nucleus basalis is the production and release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in memory and learning. The neurons in the nucleus basalis send projections to the cerebral cortex, where they release acetylcholine to modulate cortical activity.
Clinical significance[edit]
The nucleus basalis is implicated in several neurological disorders. In Alzheimer's disease, there is a significant loss of neurons in the nucleus basalis, leading to a decrease in acetylcholine production. This decrease is thought to contribute to the memory loss and cognitive decline seen in this disease. Similarly, in Parkinson's disease, there is a degeneration of neurons in the nucleus basalis, which may contribute to the cognitive symptoms of this disorder.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />
|
|
|
-
Substantia innominata MRI
-
Nucleus basalis of Meynert - Intermediate Magnification
-
Nucleus basalis of Meynert - Low Magnification
-
Nucleus basalis of Meynert - Very Low Magnification
-
Nucleus basalis of Meynert - Very High Magnification
-
Cholinergic neurons of the nucleus basalis of Meynert