Sternocostal triangle: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
[[Category:Medical Terminology]] | [[Category:Medical Terminology]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
= Sternocostal triangle = | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Gray391.png | |||
File:Diaphragma.png | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 02:07, 17 February 2025
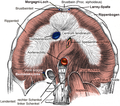
Sternocostal Triangle is a term used in anatomy to describe a specific region of the human body. It is also known as the inferior thoracic aperture or the thoracic outlet.
Etymology[edit]
The term "sternocostal" is derived from the Latin words "sternum" meaning chest bone and "costa" meaning rib. The "triangle" refers to the shape of this anatomical region.
Anatomy[edit]
The sternocostal triangle is formed by the sternum, the costal cartilages of the ribs, and the diaphragm. It is located at the lower end of the thoracic cavity, and it serves as the exit point for structures that pass between the thorax and the abdomen.
The sternocostal triangle is bordered anteriorly by the xiphoid process of the sternum, posteriorly by the body of the twelfth thoracic vertebra, and laterally by the costal margins formed by the costal cartilages of the seventh to tenth ribs.
Clinical Significance[edit]
The sternocostal triangle is clinically significant as it is the site where several important structures pass from the thorax to the abdomen. These include the esophagus, the vagus nerves, the aorta, and the inferior vena cava. Any pathological condition affecting these structures can potentially affect the sternocostal triangle.