Upper subscapular nerve: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Upper Subscapular Nerve == | |||
The ''' | The '''upper subscapular nerve''' is a nerve that arises from the posterior cord of the [[brachial plexus]]. It is responsible for innervating the upper part of the [[subscapularis muscle]], which is one of the muscles of the [[rotator cuff]] in the shoulder. | ||
== | == Anatomy == | ||
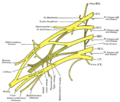
The | The upper subscapular nerve originates from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus, which is formed by the union of the posterior divisions of the upper, middle, and lower trunks. It typically arises from the fifth and sixth cervical nerves (C5 and C6). | ||
[[File:Gray807.png|thumb|right|Diagram of the brachial plexus, showing the origin of the upper subscapular nerve.]] | |||
The | The nerve travels posteriorly and enters the subscapularis muscle, providing motor innervation to its upper portion. The subscapularis muscle is located on the anterior surface of the scapula and plays a crucial role in the internal rotation of the arm. | ||
==Function== | == Function == | ||
The primary function of the upper subscapular nerve is to | The primary function of the upper subscapular nerve is to supply motor innervation to the upper part of the subscapularis muscle. This muscle is involved in the internal rotation of the humerus and stabilization of the shoulder joint. | ||
==Clinical Significance== | == Clinical Significance == | ||
Injury to the upper subscapular nerve can result in weakness or paralysis of the subscapularis muscle, leading to difficulties in internally rotating the arm. Such injuries may occur due to trauma, surgical procedures, or compression by surrounding structures. | |||
==Related | == Related Structures == | ||
The upper subscapular nerve is closely associated with other nerves of the brachial plexus, including the [[lower subscapular nerve]] and the [[thoracodorsal nerve]]. These nerves also contribute to the innervation of the shoulder and upper back muscles. | |||
[[ | [[File:Brachial_plexus.svg|thumb|right|The brachial plexus, with the upper subscapular nerve highlighted.]] | ||
{{ | == Related Pages == | ||
* [[Brachial plexus]] | |||
* [[Subscapularis muscle]] | |||
* [[Rotator cuff]] | |||
* [[Shoulder joint]] | |||
== References == | |||
* Moore, K. L., Dalley, A. F., & Agur, A. M. R. (2013). ''Clinically Oriented Anatomy''. 7th edition. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. | |||
* Standring, S. (2015). ''Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice''. 41st edition. Elsevier. | |||
[[File:Gray809.png|thumb|right|The subscapularis muscle, innervated by the upper subscapular nerve.]] | |||
{{Brachial plexus}} | |||
[[Category:Peripheral nervous system]] | |||
[[Category:Nerves of the upper limb]] | |||
== Upper subscapular nerve == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Gray807.png|Diagram of the upper subscapular nerve | |||
File:Brachial_plexus.svg|Illustration of the brachial plexus | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 02:05, 17 February 2025
Upper Subscapular Nerve[edit]
The upper subscapular nerve is a nerve that arises from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. It is responsible for innervating the upper part of the subscapularis muscle, which is one of the muscles of the rotator cuff in the shoulder.
Anatomy[edit]
The upper subscapular nerve originates from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus, which is formed by the union of the posterior divisions of the upper, middle, and lower trunks. It typically arises from the fifth and sixth cervical nerves (C5 and C6).

The nerve travels posteriorly and enters the subscapularis muscle, providing motor innervation to its upper portion. The subscapularis muscle is located on the anterior surface of the scapula and plays a crucial role in the internal rotation of the arm.
Function[edit]
The primary function of the upper subscapular nerve is to supply motor innervation to the upper part of the subscapularis muscle. This muscle is involved in the internal rotation of the humerus and stabilization of the shoulder joint.
Clinical Significance[edit]
Injury to the upper subscapular nerve can result in weakness or paralysis of the subscapularis muscle, leading to difficulties in internally rotating the arm. Such injuries may occur due to trauma, surgical procedures, or compression by surrounding structures.
Related Structures[edit]
The upper subscapular nerve is closely associated with other nerves of the brachial plexus, including the lower subscapular nerve and the thoracodorsal nerve. These nerves also contribute to the innervation of the shoulder and upper back muscles.

Related Pages[edit]
References[edit]
- Moore, K. L., Dalley, A. F., & Agur, A. M. R. (2013). Clinically Oriented Anatomy. 7th edition. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
- Standring, S. (2015). Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 41st edition. Elsevier.

| Nerve supply of the human arm | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Upper subscapular nerve[edit]
-
Diagram of the upper subscapular nerve
-
Illustration of the brachial plexus