Mental foramen: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
== Mental foramen == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Mandibular_Incisive_Canal_Highlighted.jpg|Mandibular Incisive Canal Highlighted | |||
File:Gray188.png|Gray188 | |||
File:Foramen_mentale.PNG|Foramen mentale | |||
File:Gray778.png|Gray778 | |||
File:Gray781.png|Gray781 | |||
File:Gray1003.png|Gray1003 | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 23:50, 24 February 2025
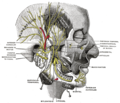
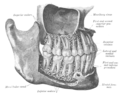
Mental Foramen
The Mental Foramen is a significant anatomical structure located in the mandible, more specifically on the body of the mandible. It is one of the several foramina found in the human skull. The term "Mental Foramen" is derived from the Latin word 'mentum', which means chin, and 'foramen' which means hole or opening.
Anatomy[edit]
The Mental Foramen is usually located in line with the longitudinal axis of the second premolar tooth, but its position can vary. It is the exit point for the mental nerve and mental artery, which provide sensory innervation and blood supply to the lower lip and chin area.
Clinical Significance[edit]
The location of the Mental Foramen is of great importance in dental procedures such as local anesthesia, implantology, and surgical interventions in the lower jaw. Misidentification or damage to the structures passing through the foramen can lead to complications such as paresthesia or hemorrhage.
Etymology[edit]
The term "Mental Foramen" is derived from the Latin word 'mentum', which means chin, and 'foramen' which means hole or opening. The term accurately describes the location and nature of this anatomical structure.