Submasseteric space: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
[[Category:Oral and maxillofacial surgery]] | [[Category:Oral and maxillofacial surgery]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Masseter_muscle_animation_small.gif|Animation of the masseter muscle | |||
File:Masticator_space.png|Diagram of the masticator space | |||
File:Gray176.png|Anatomy of the masseter muscle | |||
File:Gray378_(masseter_highlight).png|Highlighted masseter muscle | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:56, 18 February 2025
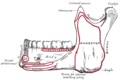
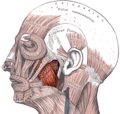
Submasseteric Space is a potential space located in the face and neck region. It is one of the deep fascial spaces of the head and neck. The submasseteric space is bounded by the masseter muscle laterally, the mandible medially, the parotid gland posteriorly, and the buccinator muscle anteriorly.
Etymology[edit]
The term "submasseteric" is derived from the Latin words "sub" meaning under and "masseter" which refers to the masseter muscle. The masseter muscle is a thick, rectangular muscle located on each side of the face. It is one of the muscles involved in mastication, or the process of chewing.
Anatomy[edit]
The submasseteric space is a potential space, meaning it is normally collapsed but can expand if filled with fluid or air. It is located between the masseter muscle and the mandible. The space is bordered by the masseter muscle laterally, the mandible medially, the parotid gland posteriorly, and the buccinator muscle anteriorly.
Clinical Significance[edit]
Infections in the submasseteric space can lead to submasseteric abscess, a condition characterized by swelling, pain, and difficulty opening the mouth. This condition is often caused by a dental infection that has spread to the submasseteric space. Treatment typically involves antibiotics and sometimes surgical drainage of the abscess.