Semispinalis muscles: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
[[Category:Muscles of the neck]] | [[Category:Muscles of the neck]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
== Semispinalis_muscles == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Semispinalis.png|Semispinalis | |||
File:Gray129.png|Gray's Anatomy Plate 129 | |||
File:Gray187.png|Gray's Anatomy Plate 187 | |||
File:Slide1ccc.JPG|Slide 1ccc | |||
File:Gray384.png|Gray's Anatomy Plate 384 | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 21:16, 23 February 2025
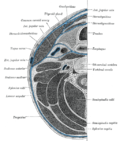
Semispinalis muscles are a group of three muscles belonging to the transversospinales. These muscles are named for their characteristic location; semi (half) spinalis (spine). They are situated in the back and neck regions of the human body. The three muscles in this group are the Semispinalis capitis, Semispinalis cervicis, and Semispinalis thoracis.
Etymology[edit]
The term "Semispinalis" is derived from the Latin words "semi", meaning half, and "spinalis", referring to the spine. This name is given due to the muscle's location and its function related to the spine.
Anatomy[edit]
The Semispinalis muscles originate from the transverse processes of the vertebrae and insert into the spinous processes of the vertebrae above. They are responsible for extending and rotating the vertebral column and head.
Semispinalis Capitis[edit]
The Semispinalis Capitis is the largest and most superficial of the three muscles. It originates from the transverse processes of the upper thoracic and lower cervical vertebrae and inserts into the occipital bone.
Semispinalis Cervicis[edit]
The Semispinalis Cervicis is located deep to the Semispinalis Capitis. It originates from the transverse processes of the upper thoracic vertebrae and inserts into the spinous processes of the cervical vertebrae.
Semispinalis Thoracis[edit]
The Semispinalis Thoracis is the deepest and smallest of the three muscles. It originates from the transverse processes of the lower thoracic vertebrae and inserts into the spinous processes of the upper thoracic and lower cervical vertebrae.
Function[edit]
The Semispinalis muscles are responsible for the extension and rotation of the vertebral column and head. They also play a role in maintaining posture and in movements of the head and neck.
Clinical Significance[edit]
Injury or strain to the Semispinalis muscles can result in back or neck pain. Treatment typically involves physical therapy, pain management, and in severe cases, surgery.