Lead(II) acetate: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
[[Category:Lead compounds]] | [[Category:Lead compounds]] | ||
[[Category:Toxic substances]] | [[Category:Toxic substances]] | ||
== Lead(II) acetate == | |||
<gallery> | |||
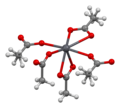
File:Lead(II)-acetate-xtal-Pb-coordination-3D-bs-17.png|Lead(II) acetate crystal structure showing Pb coordination | |||
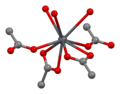
File:Lead(II)-acetate-trihydrate-xtal-Pb-coordination-3D-noH-bs-17.png|Lead(II) acetate trihydrate crystal structure showing Pb coordination | |||
File:Lead(II)-acetate-xtal-one-layer-3D-bs-17.png|Lead(II) acetate crystal structure of one layer | |||
File:Lead(II)-acetate-trihydrate-xtal-chain-3D-noH-bs-17.png|Lead(II) acetate trihydrate crystal structure showing chain | |||
File:Lead(II)-acetate-xtal-layers-3D-bs-17.png|Lead(II) acetate crystal structure showing layers | |||
File:Lead(II)-acetate-trihydrate-xtal-packing-HB-3D-noH-bs-17.png|Lead(II) acetate trihydrate crystal structure showing packing | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:30, 18 February 2025
Lead(II) acetate, also known as lead acetate or sugar of lead, is a chemical compound with the formula Pb(CH3COO)2. It is a white crystalline solid that is highly toxic and has been used historically for various purposes. In this article, we will explore the properties, uses, and safety considerations associated with lead(II) acetate.
Properties[edit]
Lead(II) acetate is soluble in water and has a sweet taste, which is why it is sometimes referred to as sugar of lead. It forms colorless crystals and has a molar mass of 325.29 g/mol. The compound has a density of 3.25 g/cm3 and a melting point of 280 °C.
Uses[edit]
Historically, lead(II) acetate has been used in various applications. One of its primary uses was in the production of lead-based pigments for paints. These pigments were widely used in the past but have been largely phased out due to the toxicity of lead compounds.
Another notable use of lead(II) acetate was in the production of hair dyes. Lead acetate was used as a coloring agent in hair dyes, particularly for darkening gray hair. However, due to concerns about lead toxicity, the use of lead acetate in hair dyes has been banned in many countries.
Safety Considerations[edit]
Lead(II) acetate is highly toxic and poses significant health risks. It can be absorbed through the skin, inhaled as dust or fumes, or ingested. Exposure to lead(II) acetate can lead to various health problems, including damage to the nervous system, kidneys, and reproductive system.
Due to its toxicity, the use of lead(II) acetate has been restricted or banned in many countries. It is important to handle this compound with extreme caution and follow proper safety protocols when working with it. Protective equipment, such as gloves and goggles, should be worn, and adequate ventilation should be provided to minimize exposure.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />
Lead(II) acetate[edit]
-
Lead(II) acetate crystal structure showing Pb coordination
-
Lead(II) acetate trihydrate crystal structure showing Pb coordination
-
Lead(II) acetate crystal structure of one layer
-
Lead(II) acetate trihydrate crystal structure showing chain
-
Lead(II) acetate crystal structure showing layers
-
Lead(II) acetate trihydrate crystal structure showing packing