Curvilinear coordinates: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
[[Category:Engineering]] | [[Category:Engineering]] | ||
[[Category:Geography]] | [[Category:Geography]] | ||
== Curvilinear coordinates gallery == | |||
<gallery> | |||
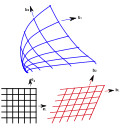
File:Curvilinear.svg|Curvilinear | |||
File:General curvilinear coordinates 1.svg|General curvilinear coordinates 1 | |||
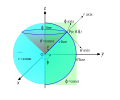
File:Spherical coordinate elements.svg|Spherical coordinate elements | |||
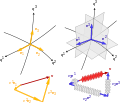
File:Vector 1-form.svg|Vector 1-form | |||
File:Local basis transformation.svg|Local basis transformation | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 05:22, 3 March 2025
Curvilinear Coordinates[edit]
Curvilinear coordinates are a system of coordinates used to describe points in space using curves instead of straight lines. Unlike Cartesian coordinates, which use orthogonal axes, curvilinear coordinates utilize curves that are not necessarily perpendicular to each other. This allows for a more flexible and versatile way of representing points in space.
Types of Curvilinear Coordinates[edit]
There are several types of curvilinear coordinate systems, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. Some of the most commonly used curvilinear coordinate systems include:
1. Cylindrical Coordinates: Cylindrical coordinates consist of a radial distance, an azimuthal angle, and a height. They are often used to describe objects with cylindrical symmetry, such as cylinders or rotating objects.
2. Spherical Coordinates: Spherical coordinates consist of a radial distance, an azimuthal angle, and a polar angle. They are particularly useful for describing points on a sphere or objects with spherical symmetry.
3. Ellipsoidal Coordinates: Ellipsoidal coordinates are used to describe points on an ellipsoid, which is a three-dimensional surface resembling a stretched sphere. They consist of three parameters: two angles and a distance from the center of the ellipsoid.
4. Parabolic Coordinates: Parabolic coordinates are a coordinate system that is particularly useful for describing objects with parabolic symmetry, such as parabolic reflectors or antennas. They consist of two parameters: a radial distance and an angle.
Applications[edit]
Curvilinear coordinates find applications in various fields of science and engineering. Some notable applications include:
1. Physics: Curvilinear coordinates are extensively used in physics, especially in the study of electromagnetism, fluid dynamics, and general relativity. They provide a convenient way to describe the behavior of physical systems in curved spaces.
2. Engineering: Curvilinear coordinates are commonly used in engineering disciplines such as structural analysis, heat transfer, and fluid mechanics. They allow engineers to model and analyze complex systems with curved geometries more accurately.
3. Geography: Curvilinear coordinates are used in geographic information systems (GIS) to represent and analyze spatial data. They enable the accurate representation of curved surfaces, such as the Earth's surface, and facilitate various geospatial analyses.
Advantages and Limitations[edit]
Curvilinear coordinates offer several advantages over Cartesian coordinates in certain situations. They provide a more natural representation for objects with curved geometries and can simplify the mathematical description of physical phenomena in curved spaces. Additionally, curvilinear coordinates often lead to simpler equations and more efficient numerical methods for solving problems.
However, curvilinear coordinates also have some limitations. They can be more challenging to work with mathematically, especially when it comes to differentiation and integration. Additionally, the choice of a specific curvilinear coordinate system may depend on the problem at hand, and different coordinate systems may be more suitable for different applications.
Conclusion[edit]
Curvilinear coordinates provide a powerful tool for describing points in space using curves instead of straight lines. They offer a more flexible and versatile way of representing objects with curved geometries and find applications in various scientific and engineering fields. While they have advantages over Cartesian coordinates in certain situations, they also come with their own challenges and limitations. Understanding and utilizing curvilinear coordinates can greatly enhance our ability to model and analyze complex systems in curved spaces.
See Also[edit]
- Cartesian coordinates
- Coordinate system
- Orthogonal coordinates
- Transformation matrix
- Vector calculus
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
Curvilinear coordinates gallery[edit]
-
Curvilinear
-
General curvilinear coordinates 1
-
Spherical coordinate elements
-
Vector 1-form
-
Local basis transformation