Valgus deformity: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Valgus deformity | |||
| image = [[File:valgus.jpg]] | |||
| caption = X-ray showing valgus deformity of the knee | |||
| field = [[Orthopedics]] | |||
| synonyms = Valgus alignment | |||
| symptoms = [[Joint pain]], [[instability]], [[gait abnormalities]] | |||
| complications = [[Osteoarthritis]], [[ligament injury]] | |||
| onset = Can be congenital or acquired | |||
| duration = Chronic | |||
| causes = [[Genetic factors]], [[trauma]], [[arthritis]] | |||
| risks = [[Obesity]], [[age]], [[previous injury]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Physical examination]], [[X-ray]], [[MRI]] | |||
| differential = [[Varus deformity]], [[joint dislocation]] | |||
| treatment = [[Physical therapy]], [[orthotic devices]], [[surgery]] | |||
| prognosis = Varies depending on severity and treatment | |||
| frequency = Common in [[adults]] and [[children]] | |||
}} | |||
== Valgus and Varus Deformities: An Overview == | == Valgus and Varus Deformities: An Overview == | ||
[[File:Child with talipes valgus and talipes varus Wellcome L0066988.jpg|left|thumb|220px|Illustration comparing Valgus (left) and Varus (right) deformities.]] | |||
[[File:Child with talipes valgus and talipes varus Wellcome L0066988.jpg|thumb | |||
A '''valgus deformity''' represents an abnormal anatomical alignment where the bone segment distal to a joint is directed away from the body's midline, typically described as an outward angling. In contrast, a '''varus deformity''' is its antithesis, with the bone angling inwards, towards the central axis of the body. | A '''valgus deformity''' represents an abnormal anatomical alignment where the bone segment distal to a joint is directed away from the body's midline, typically described as an outward angling. In contrast, a '''varus deformity''' is its antithesis, with the bone angling inwards, towards the central axis of the body. | ||
== Understanding Valgus Deformity == | == Understanding Valgus Deformity == | ||
=== Definition === | === Definition === | ||
In a valgus deformity, the distal part of a bone or joint is angled outward. This means it angles laterally, away from the body's midline. | In a valgus deformity, the distal part of a bone or joint is angled outward. This means it angles laterally, away from the body's midline. | ||
[[File:Congenital deformity of the feet Wellcome L0062992.jpg|left|thumb|180px|Representation of a Valgus deformity.]] | |||
[[File:Congenital deformity of the feet Wellcome L0062992.jpg|thumb | |||
=== Common Manifestations === | === Common Manifestations === | ||
The most commonly recognized form of valgus deformity in humans is the '''genu valgum''' or more colloquially termed, '''knock-knee'''. In this condition, when standing with the feet together, the individual's knees touch or overlap, but their ankles do not. | The most commonly recognized form of valgus deformity in humans is the '''genu valgum''' or more colloquially termed, '''knock-knee'''. In this condition, when standing with the feet together, the individual's knees touch or overlap, but their ankles do not. | ||
== Understanding Varus Deformity == | == Understanding Varus Deformity == | ||
=== Definition === | === Definition === | ||
Varus deformity, on the other hand, refers to the inward angulation of the distal segment of a bone or joint. This angulation is directed medially, moving closer to the center of the body. | Varus deformity, on the other hand, refers to the inward angulation of the distal segment of a bone or joint. This angulation is directed medially, moving closer to the center of the body. | ||
=== Common Manifestations === | === Common Manifestations === | ||
The classic representation of a varus deformity in the lower limbs is the '''genu varum''', often called '''bowleg'''. In this condition, an individual standing with their ankles together would show a distinct gap between the knees. | The classic representation of a varus deformity in the lower limbs is the '''genu varum''', often called '''bowleg'''. In this condition, an individual standing with their ankles together would show a distinct gap between the knees. | ||
== Causes of Valgus Deformity == | == Causes of Valgus Deformity == | ||
Valgus deformities can manifest due to a variety of reasons: | Valgus deformities can manifest due to a variety of reasons: | ||
* '''Arthritis of the Knee''': Progressive degeneration of the knee joint due to arthritis can lead to valgus knee. | * '''Arthritis of the Knee''': Progressive degeneration of the knee joint due to arthritis can lead to valgus knee. | ||
* '''Traumatic Injuries''': Accidents or injuries can damage the joint and surrounding tissues, leading to a misalignment in the form of a valgus deformity. | * '''Traumatic Injuries''': Accidents or injuries can damage the joint and surrounding tissues, leading to a misalignment in the form of a valgus deformity. | ||
* '''Congenital Conditions''': Some individuals may be born with conditions that predispose them to develop valgus alignments. | * '''Congenital Conditions''': Some individuals may be born with conditions that predispose them to develop valgus alignments. | ||
* '''Other Pathological Conditions''': Certain diseases and conditions can weaken or damage joints, resulting in valgus deformities. | * '''Other Pathological Conditions''': Certain diseases and conditions can weaken or damage joints, resulting in valgus deformities. | ||
== Management and Treatment == | == Management and Treatment == | ||
Treatment of valgus or varus deformities is determined by the underlying cause, severity, and associated symptoms: | Treatment of valgus or varus deformities is determined by the underlying cause, severity, and associated symptoms: | ||
* '''Physical Therapy''': Therapeutic exercises can help strengthen muscles and improve joint alignment. | * '''Physical Therapy''': Therapeutic exercises can help strengthen muscles and improve joint alignment. | ||
* '''Orthotic Devices''': Braces or shoe inserts might be recommended to correct or stabilize the deformity. | * '''Orthotic Devices''': Braces or shoe inserts might be recommended to correct or stabilize the deformity. | ||
* '''Surgery''': Severe deformities, particularly those causing pain or functional impairment, may require surgical intervention. | * '''Surgery''': Severe deformities, particularly those causing pain or functional impairment, may require surgical intervention. | ||
== Conclusion == | == Conclusion == | ||
Both valgus and varus deformities are notable anatomical misalignments that can impact an individual's mobility, functionality, and overall quality of life. Recognizing these deformities and understanding their underlying causes are paramount in ensuring effective treatment and management. | Both valgus and varus deformities are notable anatomical misalignments that can impact an individual's mobility, functionality, and overall quality of life. Recognizing these deformities and understanding their underlying causes are paramount in ensuring effective treatment and management. | ||
== See Also == | == See Also == | ||
* [[Orthopedic Disorders]] | * [[Orthopedic Disorders]] | ||
* [[Joint Anatomy and Physiology]] | * [[Joint Anatomy and Physiology]] | ||
* [[Physical Therapy in Musculoskeletal Disorders]] | * [[Physical Therapy in Musculoskeletal Disorders]] | ||
[[Category: Orthopedics|Valgus and Varus Deformities]] | [[Category: Orthopedics|Valgus and Varus Deformities]] | ||
[[Category: Musculoskeletal Disorders|Valgus and Varus Deformities]] | [[Category: Musculoskeletal Disorders|Valgus and Varus Deformities]] | ||
[[Category: Anatomy|Valgus and Varus Deformities]] | [[Category: Anatomy|Valgus and Varus Deformities]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 18:09, 12 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Valgus deformity | |
|---|---|
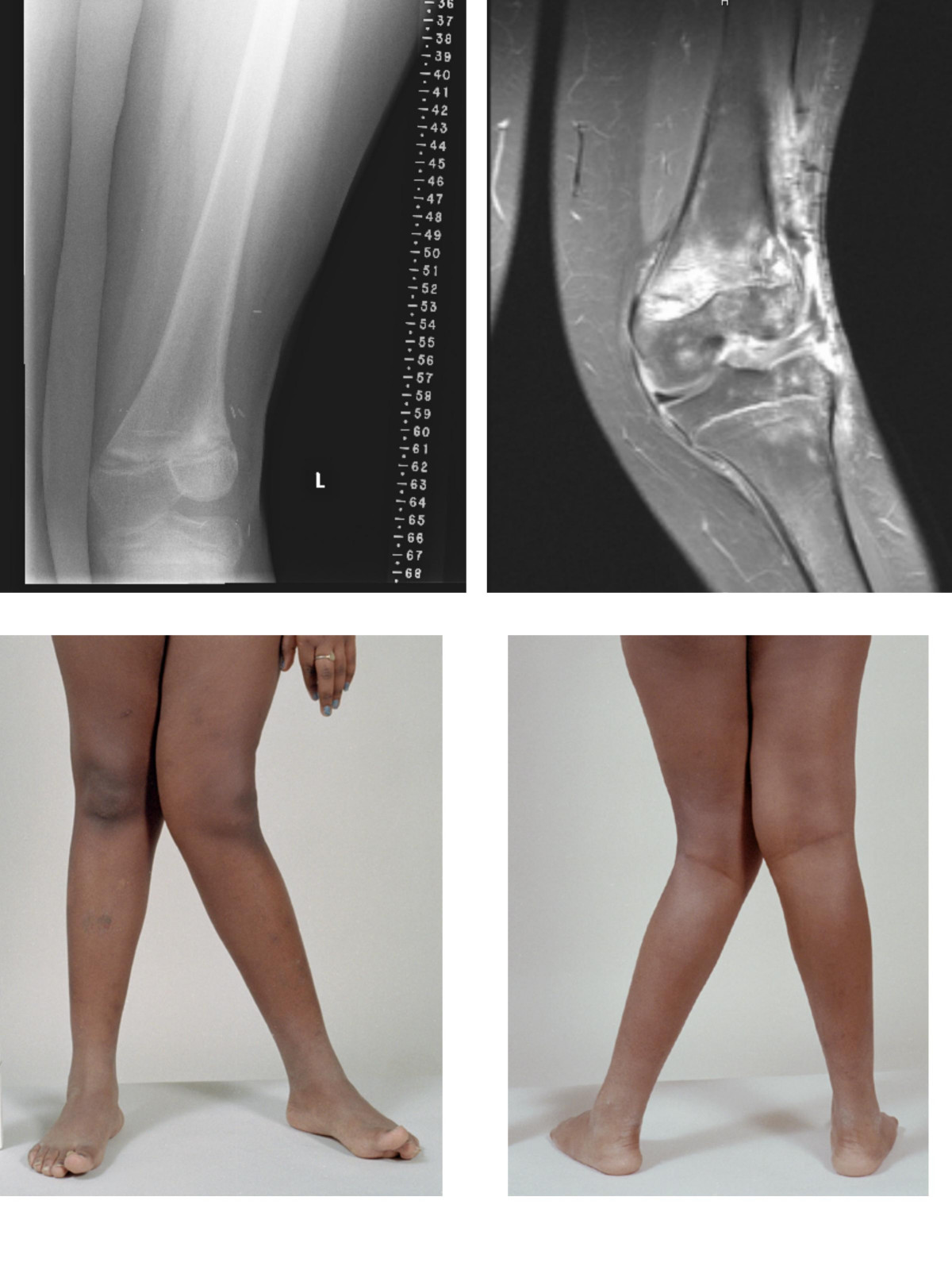
| |
| Synonyms | Valgus alignment |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Joint pain, instability, gait abnormalities |
| Complications | Osteoarthritis, ligament injury |
| Onset | Can be congenital or acquired |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetic factors, trauma, arthritis |
| Risks | Obesity, age, previous injury |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, X-ray, MRI |
| Differential diagnosis | Varus deformity, joint dislocation |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Physical therapy, orthotic devices, surgery |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Varies depending on severity and treatment |
| Frequency | Common in adults and children |
| Deaths | N/A |
Valgus and Varus Deformities: An Overview[edit]

A valgus deformity represents an abnormal anatomical alignment where the bone segment distal to a joint is directed away from the body's midline, typically described as an outward angling. In contrast, a varus deformity is its antithesis, with the bone angling inwards, towards the central axis of the body.
Understanding Valgus Deformity[edit]
Definition[edit]
In a valgus deformity, the distal part of a bone or joint is angled outward. This means it angles laterally, away from the body's midline.

Common Manifestations[edit]
The most commonly recognized form of valgus deformity in humans is the genu valgum or more colloquially termed, knock-knee. In this condition, when standing with the feet together, the individual's knees touch or overlap, but their ankles do not.
Understanding Varus Deformity[edit]
Definition[edit]
Varus deformity, on the other hand, refers to the inward angulation of the distal segment of a bone or joint. This angulation is directed medially, moving closer to the center of the body.
Common Manifestations[edit]
The classic representation of a varus deformity in the lower limbs is the genu varum, often called bowleg. In this condition, an individual standing with their ankles together would show a distinct gap between the knees.
Causes of Valgus Deformity[edit]
Valgus deformities can manifest due to a variety of reasons:
- Arthritis of the Knee: Progressive degeneration of the knee joint due to arthritis can lead to valgus knee.
- Traumatic Injuries: Accidents or injuries can damage the joint and surrounding tissues, leading to a misalignment in the form of a valgus deformity.
- Congenital Conditions: Some individuals may be born with conditions that predispose them to develop valgus alignments.
- Other Pathological Conditions: Certain diseases and conditions can weaken or damage joints, resulting in valgus deformities.
Management and Treatment[edit]
Treatment of valgus or varus deformities is determined by the underlying cause, severity, and associated symptoms:
- Physical Therapy: Therapeutic exercises can help strengthen muscles and improve joint alignment.
- Orthotic Devices: Braces or shoe inserts might be recommended to correct or stabilize the deformity.
- Surgery: Severe deformities, particularly those causing pain or functional impairment, may require surgical intervention.
Conclusion[edit]
Both valgus and varus deformities are notable anatomical misalignments that can impact an individual's mobility, functionality, and overall quality of life. Recognizing these deformities and understanding their underlying causes are paramount in ensuring effective treatment and management.


