Interphalangeal joints of the hand: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:DIP,_PIP_and_MCP_joints_of_hand.jpg|DIP, PIP, and MCP joints of hand|thumb]] | |||
[[File:814_Radiograph_of_Hand.jpg|Radiograph of hand|thumb|left]] | |||
[[File:Slide1tyty.JPG|Interphalangeal joints of the hand|left|thumb]] | |||
[[File:Gray337.png|Interphalangeal joints of the hand|thumb]] | |||
'''Interphalangeal joints of the hand''' are the hinge joints located between the [[phalanges]] of the [[human hand]]. The interphalangeal joints are all hinge joints, a type of synovial joint that allows motion in one plane only. | '''Interphalangeal joints of the hand''' are the hinge joints located between the [[phalanges]] of the [[human hand]]. The interphalangeal joints are all hinge joints, a type of synovial joint that allows motion in one plane only. | ||
| Line 21: | Line 25: | ||
* [[Rheumatoid arthritis]] | * [[Rheumatoid arthritis]] | ||
* [[Psoriatic arthritis]] | * [[Psoriatic arthritis]] | ||
[[Category:Anatomy]] | [[Category:Anatomy]] | ||
[[Category:Joints]] | [[Category:Joints]] | ||
[[Category:Hand]] | [[Category:Hand]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 18:26, 2 June 2025



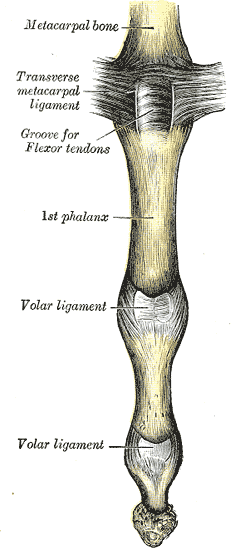
Interphalangeal joints of the hand are the hinge joints located between the phalanges of the human hand. The interphalangeal joints are all hinge joints, a type of synovial joint that allows motion in one plane only.
Etymology[edit]
The term "interphalangeal" comes from "inter-", a prefix meaning "between", and "phalangeal", which pertains to the phalanges (the bones of the fingers and toes).
Anatomy[edit]
The interphalangeal joints of the hand are divided into two categories: the proximal interphalangeal joints (PIPs) and the distal interphalangeal joints (DIPs). The PIPs are the joints in the middle knuckles of the fingers, while the DIPs are the joints closest to the end of the fingers.
Each interphalangeal joint is surrounded by a joint capsule, and the bones that form the joint are covered by articular cartilage.
Function[edit]
The interphalangeal joints of the hand allow for flexion and extension of the fingers, which is essential for many tasks involving the hands.
Clinical significance[edit]
Conditions that can affect the interphalangeal joints of the hand include osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and psoriatic arthritis. These conditions can cause pain, stiffness, and reduced function in the joints.


