Pseudomonas infection: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Pseudomonas infection | |||
| image = [[File:Pseudomonas_aeruginosa_SEM.jpg|alt=Pseudomonas aeruginosa SEM|upright=1.2]] | |||
| caption = ''[[Pseudomonas aeruginosa]]'' under a scanning electron microscope | |||
| field = [[Infectious disease]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Fever]], [[chills]], [[fatigue]], [[muscle pain]], [[joint pain]], [[cough]], [[shortness of breath]], [[skin rash]], [[ear pain]], [[eye pain]] | |||
| complications = [[Sepsis]], [[pneumonia]], [[urinary tract infection]], [[endocarditis]], [[osteomyelitis]] | |||
| onset = Varies depending on the site of infection | |||
| duration = Can be acute or chronic | |||
| causes = ''[[Pseudomonas aeruginosa]]'' | |||
| risks = [[Immunocompromised]], [[hospitalization]], [[cystic fibrosis]], [[burns]], [[catheter use]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Culture (microbiology)|Culture]], [[PCR]], [[imaging studies]] | |||
| differential = [[Staphylococcal infection]], [[Klebsiella infection]], [[Escherichia coli infection]] | |||
| prevention = [[Hand hygiene]], [[sterilization]], [[antibiotic stewardship]] | |||
| treatment = [[Antibiotics]] (e.g., [[piperacillin/tazobactam]], [[ciprofloxacin]], [[ceftazidime]]) | |||
| medication = [[Antibiotics]] | |||
| prognosis = Varies; can be severe in [[immunocompromised]] individuals | |||
| frequency = Common in [[hospital-acquired infections]] | |||
}} | |||
[[File:Diagnostic_algorithm_of_possible_bacterial_infection.png|Diagnostic algorithm of possible bacterial infection|thumb|left]] | |||
'''Pseudomonas Infection''' is a type of bacterial infection caused by the [[Pseudomonas aeruginosa]] bacterium. This bacterium is commonly found in the environment, such as in soil and water, but can also be found on the skin of some healthy individuals. | '''Pseudomonas Infection''' is a type of bacterial infection caused by the [[Pseudomonas aeruginosa]] bacterium. This bacterium is commonly found in the environment, such as in soil and water, but can also be found on the skin of some healthy individuals. | ||
== Causes and Risk Factors == | == Causes and Risk Factors == | ||
Pseudomonas infections are caused by exposure to the Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacterium. This bacterium is opportunistic, meaning it typically only causes infections in individuals with weakened [[immune system|immune systems]] or those with wounds or burns that provide an entry point for the bacteria. | Pseudomonas infections are caused by exposure to the Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacterium. This bacterium is opportunistic, meaning it typically only causes infections in individuals with weakened [[immune system|immune systems]] or those with wounds or burns that provide an entry point for the bacteria. | ||
Risk factors for Pseudomonas infections include hospitalization, especially in intensive care units, use of invasive devices such as [[catheter|catheters]] or [[ventilator|ventilators]], and underlying health conditions such as [[cystic fibrosis]] or [[HIV/AIDS]]. | Risk factors for Pseudomonas infections include hospitalization, especially in intensive care units, use of invasive devices such as [[catheter|catheters]] or [[ventilator|ventilators]], and underlying health conditions such as [[cystic fibrosis]] or [[HIV/AIDS]]. | ||
== Symptoms == | == Symptoms == | ||
The symptoms of a Pseudomonas infection can vary greatly depending on the area of the body that is infected. Common symptoms can include fever, chills, fatigue, and a general feeling of illness. If the infection is in the lungs, symptoms can include cough, shortness of breath, and chest pain. If the infection is in the skin, symptoms can include redness, swelling, and pain at the site of the infection. | The symptoms of a Pseudomonas infection can vary greatly depending on the area of the body that is infected. Common symptoms can include fever, chills, fatigue, and a general feeling of illness. If the infection is in the lungs, symptoms can include cough, shortness of breath, and chest pain. If the infection is in the skin, symptoms can include redness, swelling, and pain at the site of the infection. | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
Diagnosis of a Pseudomonas infection typically involves taking a sample of body fluid or tissue and sending it to a laboratory for testing. The laboratory will attempt to grow the bacteria from the sample, a process known as [[culture (biology)|culture]], to confirm the presence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. | Diagnosis of a Pseudomonas infection typically involves taking a sample of body fluid or tissue and sending it to a laboratory for testing. The laboratory will attempt to grow the bacteria from the sample, a process known as [[culture (biology)|culture]], to confirm the presence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
Treatment for Pseudomonas infections typically involves antibiotics. However, Pseudomonas aeruginosa is known for its resistance to many commonly used antibiotics, making treatment more difficult. In some cases, a combination of antibiotics may be used to effectively treat the infection. | Treatment for Pseudomonas infections typically involves antibiotics. However, Pseudomonas aeruginosa is known for its resistance to many commonly used antibiotics, making treatment more difficult. In some cases, a combination of antibiotics may be used to effectively treat the infection. | ||
== Prevention == | == Prevention == | ||
Prevention of Pseudomonas infections involves good hygiene practices, such as regular hand washing, especially in healthcare settings. In hospitals, proper cleaning and sterilization of equipment, as well as the use of infection control measures, can help prevent the spread of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. | Prevention of Pseudomonas infections involves good hygiene practices, such as regular hand washing, especially in healthcare settings. In hospitals, proper cleaning and sterilization of equipment, as well as the use of infection control measures, can help prevent the spread of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. | ||
[[Category:Infectious diseases]] | [[Category:Infectious diseases]] | ||
[[Category:Bacterial diseases]] | [[Category:Bacterial diseases]] | ||
{{Infectious-disease-stub}} | {{Infectious-disease-stub}} | ||
{{Medicine-stub}} | {{Medicine-stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 05:27, 9 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Pseudomonas infection | |
|---|---|
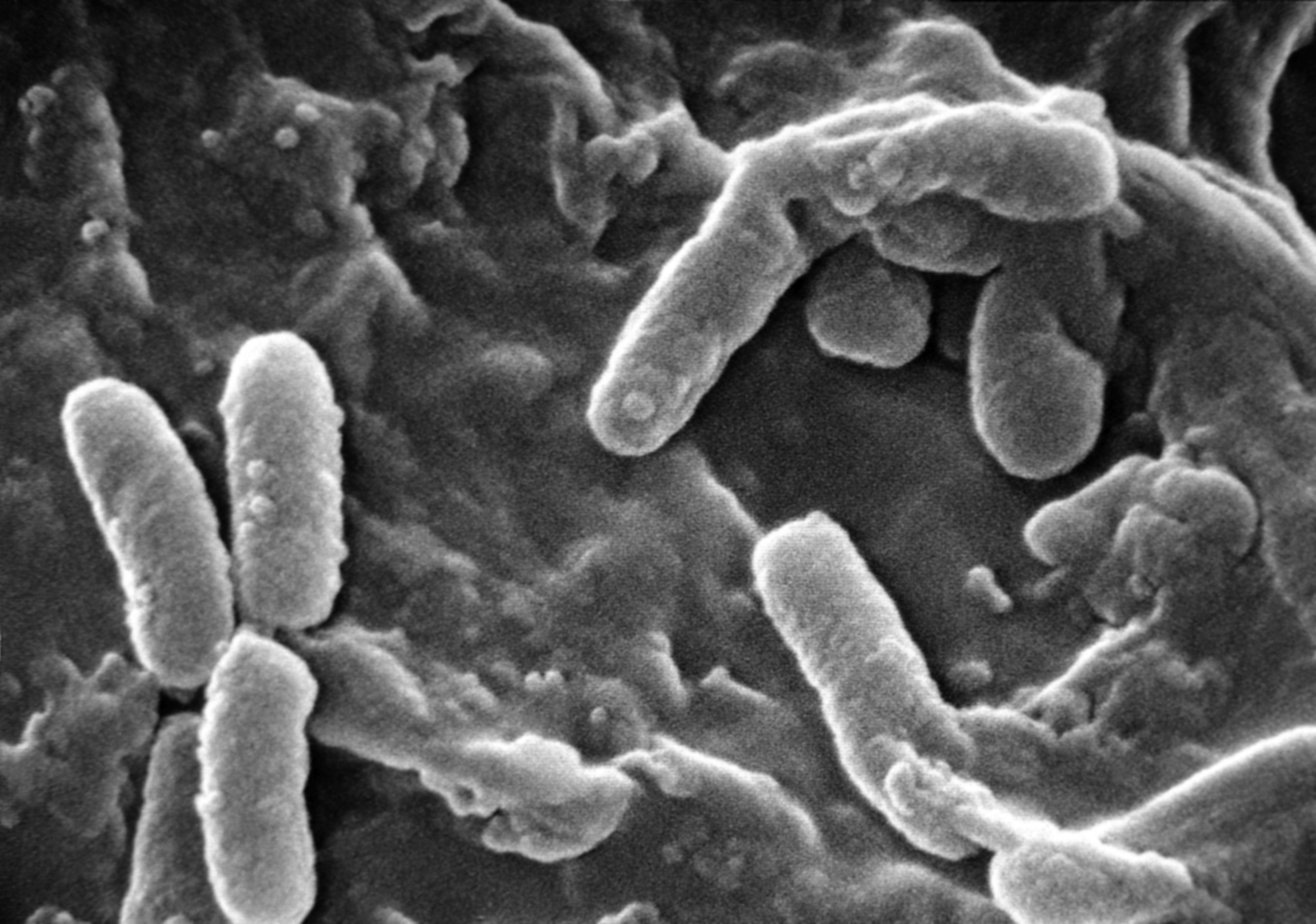
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Fever, chills, fatigue, muscle pain, joint pain, cough, shortness of breath, skin rash, ear pain, eye pain |
| Complications | Sepsis, pneumonia, urinary tract infection, endocarditis, osteomyelitis |
| Onset | Varies depending on the site of infection |
| Duration | Can be acute or chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
| Risks | Immunocompromised, hospitalization, cystic fibrosis, burns, catheter use |
| Diagnosis | Culture, PCR, imaging studies |
| Differential diagnosis | Staphylococcal infection, Klebsiella infection, Escherichia coli infection |
| Prevention | Hand hygiene, sterilization, antibiotic stewardship |
| Treatment | Antibiotics (e.g., piperacillin/tazobactam, ciprofloxacin, ceftazidime) |
| Medication | Antibiotics |
| Prognosis | Varies; can be severe in immunocompromised individuals |
| Frequency | Common in hospital-acquired infections |
| Deaths | N/A |

Pseudomonas Infection is a type of bacterial infection caused by the Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacterium. This bacterium is commonly found in the environment, such as in soil and water, but can also be found on the skin of some healthy individuals.
Causes and Risk Factors[edit]
Pseudomonas infections are caused by exposure to the Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacterium. This bacterium is opportunistic, meaning it typically only causes infections in individuals with weakened immune systems or those with wounds or burns that provide an entry point for the bacteria. Risk factors for Pseudomonas infections include hospitalization, especially in intensive care units, use of invasive devices such as catheters or ventilators, and underlying health conditions such as cystic fibrosis or HIV/AIDS.
Symptoms[edit]
The symptoms of a Pseudomonas infection can vary greatly depending on the area of the body that is infected. Common symptoms can include fever, chills, fatigue, and a general feeling of illness. If the infection is in the lungs, symptoms can include cough, shortness of breath, and chest pain. If the infection is in the skin, symptoms can include redness, swelling, and pain at the site of the infection.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of a Pseudomonas infection typically involves taking a sample of body fluid or tissue and sending it to a laboratory for testing. The laboratory will attempt to grow the bacteria from the sample, a process known as culture, to confirm the presence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for Pseudomonas infections typically involves antibiotics. However, Pseudomonas aeruginosa is known for its resistance to many commonly used antibiotics, making treatment more difficult. In some cases, a combination of antibiotics may be used to effectively treat the infection.
Prevention[edit]
Prevention of Pseudomonas infections involves good hygiene practices, such as regular hand washing, especially in healthcare settings. In hospitals, proper cleaning and sterilization of equipment, as well as the use of infection control measures, can help prevent the spread of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.

This article is a infectious disease stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
