Small for gestational age: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Small for gestational age | |||
| image = [[File:Weight_vs_gestational_Age.jpg]] | |||
| caption = Graph showing weight versus gestational age | |||
| field = [[Pediatrics]] | |||
| synonyms = SGA | |||
| symptoms = Birth weight below the 10th percentile for gestational age | |||
| complications = [[Hypoglycemia]], [[hypothermia]], [[polycythemia]], [[impaired neurodevelopment]] | |||
| onset = [[Prenatal]] | |||
| duration = Varies | |||
| causes = [[Placental insufficiency]], [[genetic factors]], [[maternal malnutrition]], [[infections]] | |||
| risks = [[Preterm birth]], [[stillbirth]], [[developmental delays]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Ultrasound]], [[fundal height measurement]], [[Doppler flow studies]] | |||
| differential = [[Intrauterine growth restriction]], [[preterm birth]], [[congenital anomalies]] | |||
| prevention = [[Prenatal care]], [[nutritional support]], [[smoking cessation]] | |||
| treatment = [[Nutritional support]], [[temperature regulation]], [[monitoring for complications]] | |||
| frequency = 3-10% of pregnancies | |||
| deaths = Increased risk of perinatal mortality | |||
}} | |||
''Small for gestational age''' (SGA) refers to an infant born with a weight less than the 10th percentile for gestational age. It is a term used to describe a condition that can occur during pregnancy when a baby does not grow to its expected size in the womb. | |||
== Causes == | == Causes == | ||
The most common cause of SGA is a problem with the placenta. The placenta is the tissue that joins the mother and fetus, carrying oxygen and nutrients to the baby and permitting the release of waste products from the baby. Other causes can include infections and birth defects. It can also be caused by health problems in the mother, such as: | The most common cause of SGA is a problem with the placenta. The placenta is the tissue that joins the mother and fetus, carrying oxygen and nutrients to the baby and permitting the release of waste products from the baby. Other causes can include infections and birth defects. It can also be caused by health problems in the mother, such as: | ||
| Line 9: | Line 28: | ||
* Preeclampsia | * Preeclampsia | ||
* Smoking, alcohol use, or drug use during pregnancy | * Smoking, alcohol use, or drug use during pregnancy | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
SGA may be suspected during pregnancy if the mother's weight gain is slow or if the size of the uterus is smaller than expected. This can be confirmed with an ultrasound. After birth, the baby's weight, length, and head circumference are measured and compared to other babies of the same gestational age. | SGA may be suspected during pregnancy if the mother's weight gain is slow or if the size of the uterus is smaller than expected. This can be confirmed with an ultrasound. After birth, the baby's weight, length, and head circumference are measured and compared to other babies of the same gestational age. | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
Treatment depends on the cause of the SGA. If the mother's health is responsible, treatment may involve managing the underlying condition. If the problem is with the placenta, the baby may need to be delivered early. After birth, the baby may need to be cared for in a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU). | Treatment depends on the cause of the SGA. If the mother's health is responsible, treatment may involve managing the underlying condition. If the problem is with the placenta, the baby may need to be delivered early. After birth, the baby may need to be cared for in a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU). | ||
== Prognosis == | == Prognosis == | ||
Babies who are SGA may have problems with certain skills and development and may be at risk for certain health conditions later in life, such as diabetes and heart disease. However, with appropriate care and treatment, many SGA babies catch up in height and weight by early childhood. | Babies who are SGA may have problems with certain skills and development and may be at risk for certain health conditions later in life, such as diabetes and heart disease. However, with appropriate care and treatment, many SGA babies catch up in height and weight by early childhood. | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
* [[Intrauterine growth restriction]] | * [[Intrauterine growth restriction]] | ||
* [[Premature birth]] | * [[Premature birth]] | ||
* [[Low birth weight]] | * [[Low birth weight]] | ||
[[Category:Obstetrics]] | [[Category:Obstetrics]] | ||
[[Category:Neonatology]] | [[Category:Neonatology]] | ||
[[Category:Pediatrics]] | [[Category:Pediatrics]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 22:55, 6 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Small for gestational age | |
|---|---|
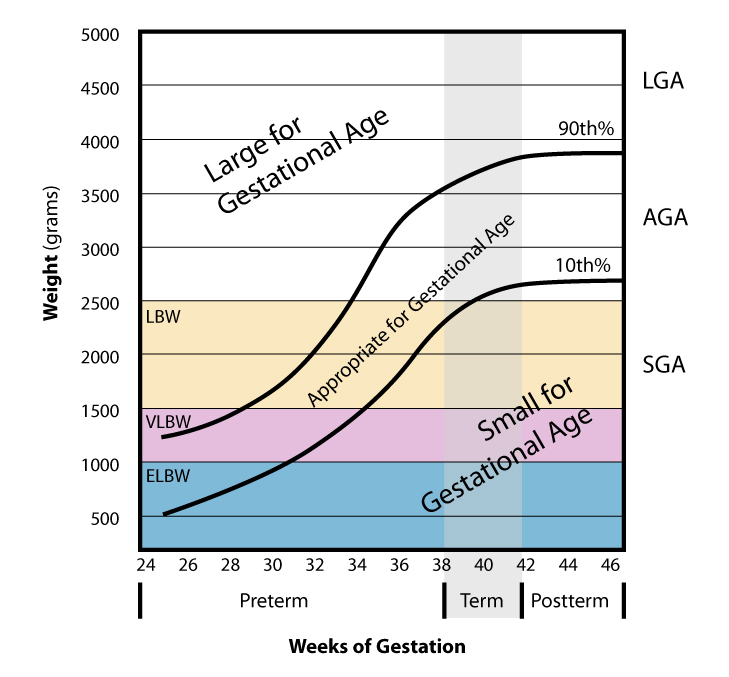
| |
| Synonyms | SGA |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Birth weight below the 10th percentile for gestational age |
| Complications | Hypoglycemia, hypothermia, polycythemia, impaired neurodevelopment |
| Onset | Prenatal |
| Duration | Varies |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Placental insufficiency, genetic factors, maternal malnutrition, infections |
| Risks | Preterm birth, stillbirth, developmental delays |
| Diagnosis | Ultrasound, fundal height measurement, Doppler flow studies |
| Differential diagnosis | Intrauterine growth restriction, preterm birth, congenital anomalies |
| Prevention | Prenatal care, nutritional support, smoking cessation |
| Treatment | Nutritional support, temperature regulation, monitoring for complications |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | N/A |
| Frequency | 3-10% of pregnancies |
| Deaths | Increased risk of perinatal mortality |
Small for gestational age' (SGA) refers to an infant born with a weight less than the 10th percentile for gestational age. It is a term used to describe a condition that can occur during pregnancy when a baby does not grow to its expected size in the womb.
Causes[edit]
The most common cause of SGA is a problem with the placenta. The placenta is the tissue that joins the mother and fetus, carrying oxygen and nutrients to the baby and permitting the release of waste products from the baby. Other causes can include infections and birth defects. It can also be caused by health problems in the mother, such as:
- Heart disease
- High blood pressure
- Kidney disease
- Malnutrition
- Preeclampsia
- Smoking, alcohol use, or drug use during pregnancy
Diagnosis[edit]
SGA may be suspected during pregnancy if the mother's weight gain is slow or if the size of the uterus is smaller than expected. This can be confirmed with an ultrasound. After birth, the baby's weight, length, and head circumference are measured and compared to other babies of the same gestational age.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment depends on the cause of the SGA. If the mother's health is responsible, treatment may involve managing the underlying condition. If the problem is with the placenta, the baby may need to be delivered early. After birth, the baby may need to be cared for in a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU).
Prognosis[edit]
Babies who are SGA may have problems with certain skills and development and may be at risk for certain health conditions later in life, such as diabetes and heart disease. However, with appropriate care and treatment, many SGA babies catch up in height and weight by early childhood.


