Frostbite: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Frostbite | |||
| image = [[File:Frost_bite.jpg]] | |||
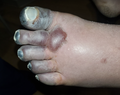
| caption = Severe frostbite affecting the fingers | |||
| field = [[Emergency medicine]] | |||
| symptoms = Cold skin, numbness, clumsiness, blistering after rewarming | |||
| complications = [[Gangrene]], [[infection]], [[hypothermia]] | |||
| onset = Gradual with exposure to cold | |||
| duration = Varies, can be permanent | |||
| causes = Exposure to extreme cold | |||
| risks = [[Alcohol consumption]], [[smoking]], [[diabetes]], [[peripheral neuropathy]] | |||
| diagnosis = Based on symptoms and physical examination | |||
| differential = [[Chilblains]], [[trench foot]], [[Raynaud's phenomenon]] | |||
| prevention = Proper clothing, avoiding prolonged exposure to cold | |||
| treatment = Rewarming, pain management, wound care, possible surgery | |||
| prognosis = Depends on severity; possible permanent damage | |||
| frequency = Common in cold climates | |||
| deaths = Rare, but possible due to complications | |||
}} | |||
{{Infobox disease | {{Infobox disease | ||
| Name = Frostbite | | Name = Frostbite | ||
| Line 14: | Line 34: | ||
| MeshID = D00562 | | MeshID = D00562 | ||
}} | }} | ||
Over-the-counter (OTC) [[drugs]] are a class of medications that can be purchased without the requirement of a doctor's [[prescription]]. They are primarily used for the treatment of common, non-serious, and self-diagnosable health conditions. | Over-the-counter (OTC) [[drugs]] are a class of medications that can be purchased without the requirement of a doctor's [[prescription]]. They are primarily used for the treatment of common, non-serious, and self-diagnosable health conditions. | ||
== Classification and Examples == | == Classification and Examples == | ||
These drugs encompass a broad spectrum of classes and offer a range of remedies for conditions such as pain, cold, allergies, constipation, and heartburn. Examples include [[analgesics]] like [[aspirin]] and [[acetaminophen]], [[antihistamines]], and [[antacids]]. OTC drugs also cover dietary supplements, vitamins, and skincare products, among others. | These drugs encompass a broad spectrum of classes and offer a range of remedies for conditions such as pain, cold, allergies, constipation, and heartburn. Examples include [[analgesics]] like [[aspirin]] and [[acetaminophen]], [[antihistamines]], and [[antacids]]. OTC drugs also cover dietary supplements, vitamins, and skincare products, among others. | ||
== Regulations == | == Regulations == | ||
The availability of OTC drugs is regulated by the country's drug regulatory authority, like the Food and Drug Administration ([[FDA]]) in the United States. These agencies classify drugs based on their safety profile, potential for misuse, and necessity for a physician's supervision during treatment. | The availability of OTC drugs is regulated by the country's drug regulatory authority, like the Food and Drug Administration ([[FDA]]) in the United States. These agencies classify drugs based on their safety profile, potential for misuse, and necessity for a physician's supervision during treatment. | ||
== Safety and Risks == | == Safety and Risks == | ||
While OTC drugs are generally safe for public consumption, misuse or overuse can lead to adverse effects or drug interactions. As such, reading and understanding the label instructions and warnings is crucial. Certain groups, such as pregnant women, children, and older adults, may be more susceptible to the risks associated with OTC drugs and should exercise caution. | While OTC drugs are generally safe for public consumption, misuse or overuse can lead to adverse effects or drug interactions. As such, reading and understanding the label instructions and warnings is crucial. Certain groups, such as pregnant women, children, and older adults, may be more susceptible to the risks associated with OTC drugs and should exercise caution. | ||
== Role in Healthcare == | == Role in Healthcare == | ||
OTC drugs play an essential role in healthcare, offering convenient, cost-effective, and immediate access to medications for minor health issues. They reduce the burden on healthcare professionals and facilities by enabling self-care and preventive care. | OTC drugs play an essential role in healthcare, offering convenient, cost-effective, and immediate access to medications for minor health issues. They reduce the burden on healthcare professionals and facilities by enabling self-care and preventive care. | ||
== Frostbite gallery == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Right foot third degree frostbite.png|Right foot third degree frostbite | |||
File:Left foot third degree frostbite.png|Left foot third degree frostbite | |||
File:Human toes, 12 days post-frostbite.jpg|Human toes, 12 days post-frostbite | |||
File:Frostbite dorsal surface feet.jpg|Frostbite dorsal surface feet | |||
File:Frostbite palmar surface feet.jpg|Frostbite palmar surface feet | |||
File:CDC winter safety infographic.ogg|CDC winter safety infographic | |||
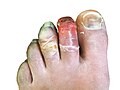
File:Human toes, 3 weeks post-frostbite.jpg|Human toes, 3 weeks post-frostbite | |||
File:Nigel Vardy Frostbite.jpg|Nigel Vardy Frostbite | |||
</gallery> | |||
== See Also == | == See Also == | ||
* [[Prescription Drug]] | * [[Prescription Drug]] | ||
* [[Pharmacy]] | * [[Pharmacy]] | ||
* [[Pharmacology]] | * [[Pharmacology]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
* "Over-the-counter (OTC) drugs." U.S. Food and Drug Administration. [https://www.fda.gov/drugs/buying-using-medicine-safely/over-counter-medicines] | * "Over-the-counter (OTC) drugs." U.S. Food and Drug Administration. [https://www.fda.gov/drugs/buying-using-medicine-safely/over-counter-medicines] | ||
* "The benefits and risks of over-the-counter medications." Johns Hopkins Medicine. [https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/the-benefits-and-risks-of-over-the-counter-medications] | * "The benefits and risks of over-the-counter medications." Johns Hopkins Medicine. [https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/the-benefits-and-risks-of-over-the-counter-medications] | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist}} | {{reflist}} | ||
{{biology-stub}} | {{biology-stub}} | ||
[[Category:Health problems]] | [[Category:Health problems]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:23, 6 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Frostbite | |
|---|---|
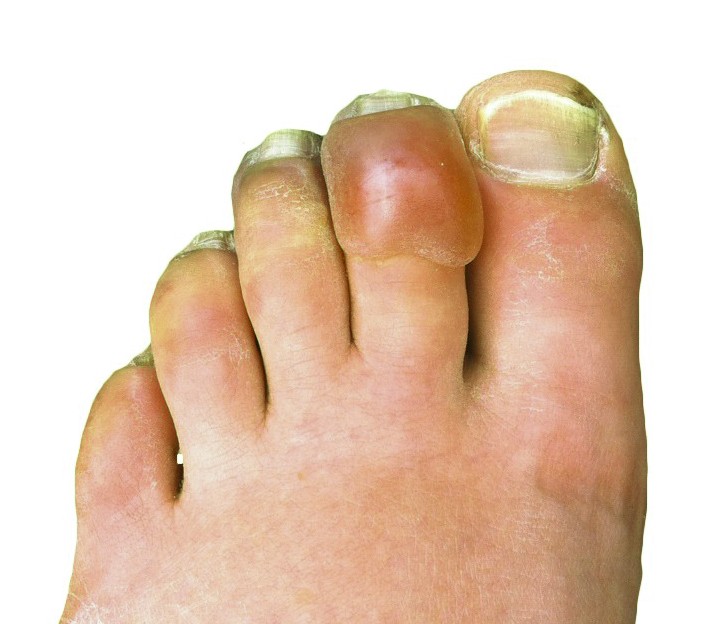
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Cold skin, numbness, clumsiness, blistering after rewarming |
| Complications | Gangrene, infection, hypothermia |
| Onset | Gradual with exposure to cold |
| Duration | Varies, can be permanent |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Exposure to extreme cold |
| Risks | Alcohol consumption, smoking, diabetes, peripheral neuropathy |
| Diagnosis | Based on symptoms and physical examination |
| Differential diagnosis | Chilblains, trench foot, Raynaud's phenomenon |
| Prevention | Proper clothing, avoiding prolonged exposure to cold |
| Treatment | Rewarming, pain management, wound care, possible surgery |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Depends on severity; possible permanent damage |
| Frequency | Common in cold climates |
| Deaths | Rare, but possible due to complications |
| Frostbite | |
|---|---|
|
|
| ICD-10 | T33
-T35 |
| ICD-9 | 991.0-991.3 |
| DiseasesDB | 31167 |
| MedlinePlus | 000057 |
| eMedicine | emerg 209 med/2815
derm/833 ped/803 |
| MeSH ID | D00562 |
Over-the-counter (OTC) drugs are a class of medications that can be purchased without the requirement of a doctor's prescription. They are primarily used for the treatment of common, non-serious, and self-diagnosable health conditions.
Classification and Examples[edit]
These drugs encompass a broad spectrum of classes and offer a range of remedies for conditions such as pain, cold, allergies, constipation, and heartburn. Examples include analgesics like aspirin and acetaminophen, antihistamines, and antacids. OTC drugs also cover dietary supplements, vitamins, and skincare products, among others.
Regulations[edit]
The availability of OTC drugs is regulated by the country's drug regulatory authority, like the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States. These agencies classify drugs based on their safety profile, potential for misuse, and necessity for a physician's supervision during treatment.
Safety and Risks[edit]
While OTC drugs are generally safe for public consumption, misuse or overuse can lead to adverse effects or drug interactions. As such, reading and understanding the label instructions and warnings is crucial. Certain groups, such as pregnant women, children, and older adults, may be more susceptible to the risks associated with OTC drugs and should exercise caution.
Role in Healthcare[edit]
OTC drugs play an essential role in healthcare, offering convenient, cost-effective, and immediate access to medications for minor health issues. They reduce the burden on healthcare professionals and facilities by enabling self-care and preventive care.
Frostbite gallery[edit]
-
Right foot third degree frostbite
-
Left foot third degree frostbite
-
Human toes, 12 days post-frostbite
-
Frostbite dorsal surface feet
-
Frostbite palmar surface feet
-
CDC winter safety infographic
-
Human toes, 3 weeks post-frostbite
-
Nigel Vardy Frostbite
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
- "Over-the-counter (OTC) drugs." U.S. Food and Drug Administration. [1]
- "The benefits and risks of over-the-counter medications." Johns Hopkins Medicine. [2]
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>