Conductive hearing loss: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Conductive hearing loss | |||
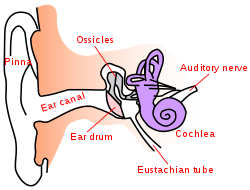
| image = [[File:Ear-anatomy-text-small-en.svg|250px]] | |||
| caption = Anatomy of the human ear | |||
| field = [[Otorhinolaryngology]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Hearing loss]], [[ear fullness]], [[tinnitus]] | |||
| complications = [[Social isolation]], [[communication difficulties]] | |||
| onset = Any age | |||
| duration = Varies | |||
| causes = [[Earwax]], [[otitis media]], [[otosclerosis]], [[ear canal obstruction]] | |||
| risks = [[Ear infections]], [[head trauma]], [[genetic factors]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Audiometry]], [[tympanometry]], [[otoscopy]] | |||
| differential = [[Sensorineural hearing loss]], [[mixed hearing loss]] | |||
| treatment = [[Hearing aids]], [[surgery]], [[earwax removal]] | |||
| prognosis = Generally good with treatment | |||
| frequency = Common | |||
}} | |||
'''Conductive hearing loss''' is a type of [[hearing loss]] that occurs when the transmission of sound from the external ear, through the middle ear to the inner ear is blocked or reduced. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including blockage in the ear canal, damage to the ear drum, or problems with the bones in the middle ear. | '''Conductive hearing loss''' is a type of [[hearing loss]] that occurs when the transmission of sound from the external ear, through the middle ear to the inner ear is blocked or reduced. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including blockage in the ear canal, damage to the ear drum, or problems with the bones in the middle ear. | ||
==Causes== | ==Causes== | ||
The most common cause of conductive hearing loss is [[otitis media]], an infection of the middle ear. Other causes can include: | The most common cause of conductive hearing loss is [[otitis media]], an infection of the middle ear. Other causes can include: | ||
* [[Earwax]] blockage | * [[Earwax]] blockage | ||
* [[Otosclerosis]], a condition where the bones in the middle ear become stiff | * [[Otosclerosis]], a condition where the bones in the middle ear become stiff | ||
| Line 9: | Line 25: | ||
* [[Cholesteatoma]], a skin growth that occurs in the middle ear | * [[Cholesteatoma]], a skin growth that occurs in the middle ear | ||
* [[Otitis externa]], an infection of the outer ear canal | * [[Otitis externa]], an infection of the outer ear canal | ||
==Symptoms== | ==Symptoms== | ||
The main symptom of conductive hearing loss is a reduction in hearing sensitivity. This can be accompanied by other symptoms such as: | The main symptom of conductive hearing loss is a reduction in hearing sensitivity. This can be accompanied by other symptoms such as: | ||
* Pain in the ear | * Pain in the ear | ||
* Discharge from the ear | * Discharge from the ear | ||
* Tinnitus, a ringing or buzzing noise in the ear | * Tinnitus, a ringing or buzzing noise in the ear | ||
* Vertigo, a sensation of spinning | * Vertigo, a sensation of spinning | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
Conductive hearing loss is diagnosed through a series of tests, including: | Conductive hearing loss is diagnosed through a series of tests, including: | ||
* [[Audiometry]], a test that measures a person's ability to hear sounds | * [[Audiometry]], a test that measures a person's ability to hear sounds | ||
* [[Tympanometry]], a test that measures the movement of the eardrum | * [[Tympanometry]], a test that measures the movement of the eardrum | ||
* [[Otoscopy]], a visual examination of the ear canal and eardrum | * [[Otoscopy]], a visual examination of the ear canal and eardrum | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
Treatment for conductive hearing loss depends on the cause. It can include: | Treatment for conductive hearing loss depends on the cause. It can include: | ||
* Medication to treat infections | * Medication to treat infections | ||
* Surgery to repair damage to the ear | * Surgery to repair damage to the ear | ||
* Hearing aids to amplify sound | * Hearing aids to amplify sound | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
* [[Sensorineural hearing loss]] | * [[Sensorineural hearing loss]] | ||
| Line 37: | Line 46: | ||
* [[Hearing loss due to age]] | * [[Hearing loss due to age]] | ||
* [[Noise-induced hearing loss]] | * [[Noise-induced hearing loss]] | ||
[[Category:Hearing loss]] | [[Category:Hearing loss]] | ||
[[Category:Otorhinolaryngology]] | [[Category:Otorhinolaryngology]] | ||
{{Medicine-stub}} | {{Medicine-stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 02:21, 5 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Conductive hearing loss | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Hearing loss, ear fullness, tinnitus |
| Complications | Social isolation, communication difficulties |
| Onset | Any age |
| Duration | Varies |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Earwax, otitis media, otosclerosis, ear canal obstruction |
| Risks | Ear infections, head trauma, genetic factors |
| Diagnosis | Audiometry, tympanometry, otoscopy |
| Differential diagnosis | Sensorineural hearing loss, mixed hearing loss |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Hearing aids, surgery, earwax removal |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Generally good with treatment |
| Frequency | Common |
| Deaths | N/A |
Conductive hearing loss is a type of hearing loss that occurs when the transmission of sound from the external ear, through the middle ear to the inner ear is blocked or reduced. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including blockage in the ear canal, damage to the ear drum, or problems with the bones in the middle ear.
Causes[edit]
The most common cause of conductive hearing loss is otitis media, an infection of the middle ear. Other causes can include:
- Earwax blockage
- Otosclerosis, a condition where the bones in the middle ear become stiff
- Damage to the eardrum
- Cholesteatoma, a skin growth that occurs in the middle ear
- Otitis externa, an infection of the outer ear canal
Symptoms[edit]
The main symptom of conductive hearing loss is a reduction in hearing sensitivity. This can be accompanied by other symptoms such as:
- Pain in the ear
- Discharge from the ear
- Tinnitus, a ringing or buzzing noise in the ear
- Vertigo, a sensation of spinning
Diagnosis[edit]
Conductive hearing loss is diagnosed through a series of tests, including:
- Audiometry, a test that measures a person's ability to hear sounds
- Tympanometry, a test that measures the movement of the eardrum
- Otoscopy, a visual examination of the ear canal and eardrum
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for conductive hearing loss depends on the cause. It can include:
- Medication to treat infections
- Surgery to repair damage to the ear
- Hearing aids to amplify sound
See also[edit]
