Turbinectomy: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Turbinectomy''' is a surgical procedure that involves the removal | {{Short description|Surgical procedure involving the removal of nasal turbinates}} | ||
'''Turbinectomy''' is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the nasal turbinates, which are structures within the nose that help to filter, warm, and humidify the air we breathe. This procedure is typically performed to alleviate nasal obstruction and improve airflow in patients with chronic nasal congestion or other nasal pathologies. | |||
==Anatomy and Function of Nasal Turbinates== | |||
The nasal turbinates are long, narrow shelves of bone that protrude into the nasal cavity. They are covered with a mucous membrane and are divided into three main types: the inferior, middle, and superior turbinates. The primary function of the turbinates is to regulate airflow and support the nasal mucosa, which plays a crucial role in filtering and humidifying the air. | |||
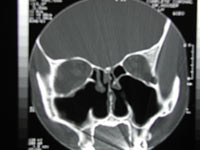
[[File:EmptyNose-AfterTotalBilateralTurbinectomy-CT.jpg|thumb|CT scan showing empty nose syndrome after total bilateral turbinectomy.]] | |||
==Indications for Turbinectomy== | |||
Turbinectomy is generally indicated for patients who suffer from chronic nasal obstruction that does not respond to medical treatment. Conditions that may necessitate a turbinectomy include: | |||
* [[Chronic rhinitis]] | |||
* [[Nasal polyps]] | |||
* [[Deviated septum]] | |||
* [[Sinusitis]] | |||
* [[Sleep apnea]] | |||
==Procedure== | ==Procedure== | ||
The turbinectomy procedure can be performed under | The turbinectomy procedure can be performed using various techniques, including traditional surgical methods and more modern approaches such as laser or radiofrequency ablation. The choice of technique depends on the specific condition being treated and the surgeon's expertise. | ||
===Traditional Surgical Turbinectomy=== | |||
In a traditional surgical turbinectomy, the surgeon removes part or all of the turbinate bone and surrounding tissue. This is usually done under general anesthesia. The goal is to reduce the size of the turbinates to improve airflow through the nasal passages. | |||
===Laser and Radiofrequency Ablation=== | |||
Laser and radiofrequency ablation are less invasive techniques that use energy to shrink the turbinates. These methods are often performed under local anesthesia and may result in less postoperative discomfort and quicker recovery times. | |||
== | ==Complications== | ||
While turbinectomy can be effective in relieving nasal obstruction, it is not without risks. Potential complications include: | |||
* [[Bleeding]] | |||
* [[Infection]] | |||
* [[Scarring]] | |||
* [[Empty nose syndrome]] | |||
==Recovery== | ==Empty Nose Syndrome== | ||
Recovery from a turbinectomy | {{Main|Empty nose syndrome}} | ||
Empty nose syndrome (ENS) is a rare but serious complication that can occur after turbinectomy. It is characterized by a paradoxical sensation of nasal obstruction despite an open nasal passage, often accompanied by dryness and crusting. ENS can significantly impact a patient's quality of life and may require further treatment. | |||
==Recovery and Prognosis== | |||
Recovery from a turbinectomy varies depending on the extent of the surgery and the technique used. Patients may experience nasal congestion, bleeding, and discomfort in the immediate postoperative period. Most patients can return to normal activities within a few weeks, although complete healing may take longer. | |||
== | ==Related pages== | ||
* [[Rhinoplasty]] | * [[Rhinoplasty]] | ||
* [[Septoplasty]] | * [[Septoplasty]] | ||
* [[Sinus Surgery | * [[Sinus surgery]] | ||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist}} | |||
==External links== | |||
* [https://www.entnet.org/ American Academy of Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery] | |||
[[Category:Otorhinolaryngology]] | [[Category:Otorhinolaryngology]] | ||
[[Category:Surgical procedures and techniques]] | |||
Latest revision as of 12:50, 31 March 2025
Surgical procedure involving the removal of nasal turbinates
Turbinectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the nasal turbinates, which are structures within the nose that help to filter, warm, and humidify the air we breathe. This procedure is typically performed to alleviate nasal obstruction and improve airflow in patients with chronic nasal congestion or other nasal pathologies.
Anatomy and Function of Nasal Turbinates[edit]
The nasal turbinates are long, narrow shelves of bone that protrude into the nasal cavity. They are covered with a mucous membrane and are divided into three main types: the inferior, middle, and superior turbinates. The primary function of the turbinates is to regulate airflow and support the nasal mucosa, which plays a crucial role in filtering and humidifying the air.
Indications for Turbinectomy[edit]
Turbinectomy is generally indicated for patients who suffer from chronic nasal obstruction that does not respond to medical treatment. Conditions that may necessitate a turbinectomy include:
Procedure[edit]
The turbinectomy procedure can be performed using various techniques, including traditional surgical methods and more modern approaches such as laser or radiofrequency ablation. The choice of technique depends on the specific condition being treated and the surgeon's expertise.
Traditional Surgical Turbinectomy[edit]
In a traditional surgical turbinectomy, the surgeon removes part or all of the turbinate bone and surrounding tissue. This is usually done under general anesthesia. The goal is to reduce the size of the turbinates to improve airflow through the nasal passages.
Laser and Radiofrequency Ablation[edit]
Laser and radiofrequency ablation are less invasive techniques that use energy to shrink the turbinates. These methods are often performed under local anesthesia and may result in less postoperative discomfort and quicker recovery times.
Complications[edit]
While turbinectomy can be effective in relieving nasal obstruction, it is not without risks. Potential complications include:
Empty Nose Syndrome[edit]
Empty nose syndrome (ENS) is a rare but serious complication that can occur after turbinectomy. It is characterized by a paradoxical sensation of nasal obstruction despite an open nasal passage, often accompanied by dryness and crusting. ENS can significantly impact a patient's quality of life and may require further treatment.
Recovery and Prognosis[edit]
Recovery from a turbinectomy varies depending on the extent of the surgery and the technique used. Patients may experience nasal congestion, bleeding, and discomfort in the immediate postoperative period. Most patients can return to normal activities within a few weeks, although complete healing may take longer.
Related pages[edit]
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>