Bone marrow examination: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Bone Marrow Examination== | |||
[[File:Site_for_procedure_of_Bone_Marrow.jpg|Site for procedure of Bone Marrow|thumb|right]] | |||
A '''bone marrow examination''' is a diagnostic procedure that involves the extraction and analysis of bone marrow tissue. This procedure is crucial for diagnosing and monitoring various [[hematological disorders]], including [[leukemia]], [[lymphoma]], and [[anemia]]. | |||
==Bone Marrow | ==Types of Bone Marrow Examination== | ||
Bone marrow examination typically involves two main types of procedures: [[bone marrow aspiration]] and [[bone marrow biopsy]]. | |||
== | ===Bone Marrow Aspiration=== | ||
Bone marrow | [[File:Bone_marrow_aspiration.jpg|Bone marrow aspiration|thumb|left]] | ||
Bone marrow aspiration involves the removal of a small amount of the liquid portion of the marrow. This procedure is often performed to evaluate the types and numbers of blood cells present in the marrow. It is particularly useful for diagnosing conditions like [[acute leukemia]] and [[aplastic anemia]]. | |||
===Bone Marrow Biopsy=== | |||
[[File:Bone_marrow_biopsy.jpg|Bone marrow biopsy|thumb|right]] | |||
A bone marrow biopsy involves the removal of a small, solid piece of bone marrow tissue. This procedure provides information about the architecture of the bone marrow and is essential for diagnosing conditions such as [[myelofibrosis]] and [[metastatic cancer]]. | |||
==Procedure== | ==Procedure== | ||
The | The bone marrow examination is typically performed under local anesthesia. The most common site for the procedure is the posterior iliac crest of the pelvis. The patient is positioned appropriately, and the area is cleaned and anesthetized. | ||
===Aspiration Procedure=== | |||
A special needle is inserted into the bone, and a syringe is used to aspirate the liquid marrow. The sample is then placed on slides for microscopic examination. | |||
===Biopsy Procedure=== | |||
[[File:Bone_marrow_biopsy_needle.jpg|Bone marrow biopsy needle|thumb|left]] | |||
For a biopsy, a larger needle is used to obtain a core of bone marrow tissue. This sample is processed and examined under a microscope to assess the cellularity and structure of the marrow. | |||
== | ==Microscopic Examination== | ||
[[File:Bone_marrow_core_biopsy_microscopy_(trephine)_H&E_panorama_by_gabriel_caponetti.jpg|Bone marrow core biopsy microscopy (trephine) H&E panorama|thumb|right]] | |||
The samples obtained from bone marrow aspiration and biopsy are stained and examined under a microscope. The examination focuses on the morphology of the cells, the presence of abnormal cells, and the overall cellularity of the marrow. | |||
== | ==Clinical Significance== | ||
Bone marrow examination is a critical tool in the diagnosis and management of hematological diseases. It helps in: | |||
* Diagnosing blood disorders such as [[leukemia]], [[lymphoma]], and [[myelodysplastic syndromes]]. | |||
* Evaluating the effectiveness of treatment for these conditions. | |||
* Investigating unexplained anemia, leukopenia, or thrombocytopenia. | |||
==Complications== | |||
While generally safe, bone marrow examination can have complications such as bleeding, infection, and pain at the biopsy site. These are rare and usually minor. | |||
==Related Pages== | |||
* [[Hematology]] | |||
* [[Leukemia]] | |||
* [[Lymphoma]] | |||
* [[Anemia]] | |||
[[Category:Medical procedures]] | |||
[[Category:Hematology]] | [[Category:Hematology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:40, 23 March 2025
Bone Marrow Examination[edit]

A bone marrow examination is a diagnostic procedure that involves the extraction and analysis of bone marrow tissue. This procedure is crucial for diagnosing and monitoring various hematological disorders, including leukemia, lymphoma, and anemia.
Types of Bone Marrow Examination[edit]
Bone marrow examination typically involves two main types of procedures: bone marrow aspiration and bone marrow biopsy.
Bone Marrow Aspiration[edit]

Bone marrow aspiration involves the removal of a small amount of the liquid portion of the marrow. This procedure is often performed to evaluate the types and numbers of blood cells present in the marrow. It is particularly useful for diagnosing conditions like acute leukemia and aplastic anemia.
Bone Marrow Biopsy[edit]

A bone marrow biopsy involves the removal of a small, solid piece of bone marrow tissue. This procedure provides information about the architecture of the bone marrow and is essential for diagnosing conditions such as myelofibrosis and metastatic cancer.
Procedure[edit]
The bone marrow examination is typically performed under local anesthesia. The most common site for the procedure is the posterior iliac crest of the pelvis. The patient is positioned appropriately, and the area is cleaned and anesthetized.
Aspiration Procedure[edit]
A special needle is inserted into the bone, and a syringe is used to aspirate the liquid marrow. The sample is then placed on slides for microscopic examination.
Biopsy Procedure[edit]
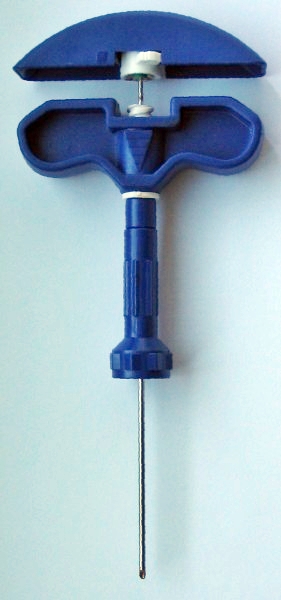
For a biopsy, a larger needle is used to obtain a core of bone marrow tissue. This sample is processed and examined under a microscope to assess the cellularity and structure of the marrow.
Microscopic Examination[edit]

The samples obtained from bone marrow aspiration and biopsy are stained and examined under a microscope. The examination focuses on the morphology of the cells, the presence of abnormal cells, and the overall cellularity of the marrow.
Clinical Significance[edit]
Bone marrow examination is a critical tool in the diagnosis and management of hematological diseases. It helps in:
- Diagnosing blood disorders such as leukemia, lymphoma, and myelodysplastic syndromes.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of treatment for these conditions.
- Investigating unexplained anemia, leukopenia, or thrombocytopenia.
Complications[edit]
While generally safe, bone marrow examination can have complications such as bleeding, infection, and pain at the biopsy site. These are rare and usually minor.