Vagus nerve: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
No edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
''' | [[File:Gray791.png|Diagram of the vagus nerve.|thumb]] | ||
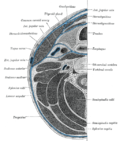
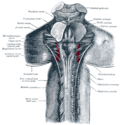
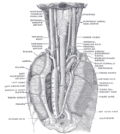
[[File:Gray793.png|Vagus nerve in the neck.|left|thumb]] | |||
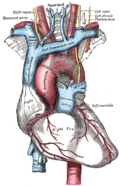
[[File:Slide6rom.JPG|Vagus nerve in the thorax.|thumb]] | |||
[[File:Slide1EBA.JPG|Vagus nerve in the abdomen.|left|thumb]] | |||
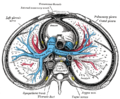
[[File:Sinoatrial_node_high_mag.jpg|Sinoatrial node, influenced by the vagus nerve.|thumb]] | |||
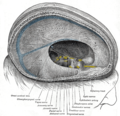
[[File:Brain_human_normal_inferior_view_with_labels_en.svg|Inferior view of the human brain showing cranial nerves.|thumb]] | |||
The '''vagus nerve''' is the tenth cranial nerve (CN X) and is a critical component of the autonomic nervous system. It is responsible for a wide range of functions, including heart rate regulation, gastrointestinal peristalsis, sweating, and muscle movements in the mouth, including speech. The vagus nerve is the longest of the cranial nerves, extending from the brainstem to the abdomen. | |||
== Anatomy == | |||
== | The vagus nerve originates in the [[medulla oblongata]] of the brainstem. It exits the skull through the [[jugular foramen]] and travels down the neck within the [[carotid sheath]], alongside the [[internal carotid artery]] and the [[internal jugular vein]]. | ||
=== Branches === | |||
The vagus nerve | The vagus nerve has several branches, including: | ||
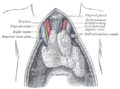
* The [[auricular branch]], which supplies sensation to the ear. | |||
* The [[pharyngeal branch]], which innervates the muscles of the pharynx. | |||
* The [[superior laryngeal nerve]], which innervates the cricothyroid muscle. | |||
* The [[recurrent laryngeal nerve]], which innervates the intrinsic muscles of the larynx. | |||
=== Function === | |||
The vagus nerve is involved in parasympathetic control of the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. It slows the heart rate, stimulates digestive secretions, and regulates the contraction of smooth muscles in the gastrointestinal tract. | |||
== Clinical | == Clinical Significance == | ||
Damage to the vagus nerve can result in a loss of | Damage to the vagus nerve can result in a variety of symptoms, including difficulty swallowing, loss of voice, and abnormal heart rate. Vagus nerve stimulation is a treatment used for epilepsy and depression. | ||
== | == Related Pages == | ||
* [[ | * [[Autonomic nervous system]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Cranial nerves]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Medulla oblongata]] | ||
* [[Jugular foramen]] | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
* Standring, S. (2016). Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 41st Edition. Elsevier. | |||
* Netter, F. H. (2014). Atlas of Human Anatomy. 6th Edition. Saunders. | |||
== | == Gallery == | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Gray384.png|Vagus nerve and its branches. | |||
File:Gray503.png|Vagus nerve in the thorax. | |||
File:Gray505.png|Vagus nerve in the abdomen. | |||
File:Gray567.png|Vagus nerve and the heart. | |||
File:Gray622.png|Vagus nerve and the stomach. | |||
File:Gray694.png|Vagus nerve and the intestines. | |||
File:Gray719.png|Vagus nerve and the liver. | |||
File:Gray792.png|Vagus nerve and the lungs. | |||
File:Gray838.png|Vagus nerve and the esophagus. | |||
File:Gray848.png|Vagus nerve and the pharynx. | |||
File:Gray1032.png|Vagus nerve and the larynx. | |||
File:Gray1174.png|Vagus nerve and the ear. | |||
File:Gray1178.png|Vagus nerve and the carotid artery. | |||
File:Internal_carotid_artery.jpg|Internal carotid artery, near the vagus nerve. | |||
</gallery> | |||
{{Cranial nerves}} | |||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Vagus Nerve}} | |||
[[Category:Vagus nerve| ]] | |||
[[Category:Cranial nerves]] | |||
[[Category:Autonomic nervous system]] | |||
[[Category:Thorax (human anatomy)]] | |||
[[Category:Abdomen]] | |||
[[Category:Gustatory system]] | |||
[[Category:Human head and neck]] | |||
[[Category:Nervous system]] | [[Category:Nervous system]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Nerves of the head and neck]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Innervation of the tongue]] | ||
[[Category:Anatomy]] | |||
[[Category:Neuroscience]] | |||
Latest revision as of 13:46, 22 March 2025






The vagus nerve is the tenth cranial nerve (CN X) and is a critical component of the autonomic nervous system. It is responsible for a wide range of functions, including heart rate regulation, gastrointestinal peristalsis, sweating, and muscle movements in the mouth, including speech. The vagus nerve is the longest of the cranial nerves, extending from the brainstem to the abdomen.
Anatomy[edit]
The vagus nerve originates in the medulla oblongata of the brainstem. It exits the skull through the jugular foramen and travels down the neck within the carotid sheath, alongside the internal carotid artery and the internal jugular vein.
Branches[edit]
The vagus nerve has several branches, including:
- The auricular branch, which supplies sensation to the ear.
- The pharyngeal branch, which innervates the muscles of the pharynx.
- The superior laryngeal nerve, which innervates the cricothyroid muscle.
- The recurrent laryngeal nerve, which innervates the intrinsic muscles of the larynx.
Function[edit]
The vagus nerve is involved in parasympathetic control of the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. It slows the heart rate, stimulates digestive secretions, and regulates the contraction of smooth muscles in the gastrointestinal tract.
Clinical Significance[edit]
Damage to the vagus nerve can result in a variety of symptoms, including difficulty swallowing, loss of voice, and abnormal heart rate. Vagus nerve stimulation is a treatment used for epilepsy and depression.
Related Pages[edit]
References[edit]
- Standring, S. (2016). Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 41st Edition. Elsevier.
- Netter, F. H. (2014). Atlas of Human Anatomy. 6th Edition. Saunders.
Gallery[edit]
-
Vagus nerve and its branches.
-
Vagus nerve in the thorax.
-
Vagus nerve in the abdomen.
-
Vagus nerve and the heart.
-
Vagus nerve and the stomach.
-
Vagus nerve and the intestines.
-
Vagus nerve and the liver.
-
Vagus nerve and the lungs.
-
Vagus nerve and the esophagus.
-
Vagus nerve and the pharynx.
-
Vagus nerve and the larynx.
-
Vagus nerve and the ear.
-
Vagus nerve and the carotid artery.
-
Internal carotid artery, near the vagus nerve.
| The cranial nerves | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|