Enpiperate: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
{{Chem-stub}} | {{Chem-stub}} | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
== Enpiperate gallery == | == Enpiperate gallery == | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
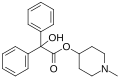
File:Enpiperate.svg|Enpiperate | File:Enpiperate.svg|Enpiperate | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 20:28, 16 March 2025
Enpiperate is a chemical compound used in the field of medicine and pharmacology. It is a pyrethroid insecticide that is used to control a variety of insect pests.
Chemical Properties[edit]
Enpiperate is a synthetic compound that belongs to the class of chemicals known as pyrethroids. Pyrethroids are synthetic versions of pyrethrins, which are natural insecticides derived from the flowers of certain species of chrysanthemum plants. Enpiperate is a non-systemic insecticide, which means it does not penetrate plant tissue but instead remains on the surface.
Uses[edit]
Enpiperate is used to control a variety of insect pests, including aphids, whiteflies, and thrips. It is used in a variety of settings, including agriculture, horticulture, and forestry. In addition to its use as an insecticide, enpiperate has also been studied for its potential use in the treatment of parasitic infections in humans.
Safety and Toxicity[edit]
Like all pyrethroids, enpiperate is toxic to insects but is generally considered safe for humans and other mammals when used properly. However, exposure to high levels of enpiperate can cause a variety of health effects, including neurological symptoms such as tremors and seizures.
Regulation[edit]
In many countries, the use of enpiperate is regulated by government agencies to ensure its safe and effective use. These agencies may set limits on the amount of enpiperate that can be used, the types of crops it can be used on, and the methods of application.
See Also[edit]
Enpiperate gallery[edit]
-
Enpiperate