4-Aminoquinoline: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:4-aminoquinoline.svg|thumb|right|Chemical structure of 4-Aminoquinoline]] | [[File:4-aminoquinoline.svg|thumb|right|Chemical structure of 4-Aminoquinoline]] | ||
[[File:4-Aminoquinoline 3D spacefill.png|3D space-filling model of 4-Aminoquinoline|thumb]] | |||
[[File:Amodiaquine.svg|Chemical structure of Amodiaquine|thumb]] | |||
'''4-Aminoquinoline''' is a class of [[chemical compounds]] that are derivatives of [[quinoline]] with an [[amino group]] at the 4-position. These compounds are known for their [[antimalarial]] properties and have been used in the treatment of [[malaria]]. | '''4-Aminoquinoline''' is a class of [[chemical compounds]] that are derivatives of [[quinoline]] with an [[amino group]] at the 4-position. These compounds are known for their [[antimalarial]] properties and have been used in the treatment of [[malaria]]. | ||
| Line 31: | Line 30: | ||
== Side Effects == | == Side Effects == | ||
The use of 4-aminoquinolines can be associated with several side effects, including gastrointestinal disturbances, [[pruritus]], and, in rare cases, [[retinopathy]]. Long-term use, particularly of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine, requires monitoring for potential ocular toxicity. | The use of 4-aminoquinolines can be associated with several side effects, including gastrointestinal disturbances, [[pruritus]], and, in rare cases, [[retinopathy]]. Long-term use, particularly of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine, requires monitoring for potential ocular toxicity. | ||
== Gallery == | == Gallery == | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
File:Chloroquine.svg|Chemical structure of Chloroquine | File:Chloroquine.svg|Chemical structure of Chloroquine | ||
File:Hydroxychloroquine.svg|Chemical structure of Hydroxychloroquine | File:Hydroxychloroquine.svg|Chemical structure of Hydroxychloroquine | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
== Related Pages == | |||
* [[Quinoline]] | |||
* [[Antimalarial drugs]] | |||
* [[Plasmodium]] | |||
* [[Malaria]] | |||
[[Category:Antimalarial agents]] | [[Category:Antimalarial agents]] | ||
[[Category:Quinolines]] | [[Category:Quinolines]] | ||
Latest revision as of 04:09, 3 March 2025



4-Aminoquinoline is a class of chemical compounds that are derivatives of quinoline with an amino group at the 4-position. These compounds are known for their antimalarial properties and have been used in the treatment of malaria.
Chemical Structure[edit]
4-Aminoquinolines are characterized by the presence of a quinoline core, which is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound, with an amino group attached to the fourth carbon of the quinoline ring. This structural modification is crucial for their biological activity.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
4-Aminoquinolines exert their antimalarial effects primarily by interfering with the parasite's ability to detoxify heme, a byproduct of hemoglobin digestion. The accumulation of toxic heme leads to the death of the Plasmodium parasites responsible for malaria.
Uses[edit]
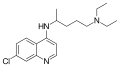
4-Aminoquinolines are primarily used in the treatment and prevention of malaria. Some of the well-known drugs in this class include:
These drugs have been used extensively in the past, although resistance to chloroquine has limited its effectiveness in many parts of the world.
Derivatives[edit]
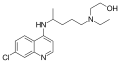
Several derivatives of 4-aminoquinoline have been developed to enhance their antimalarial activity and reduce side effects. These include:
Each of these derivatives has unique properties and uses in the treatment of malaria and other conditions.
Side Effects[edit]
The use of 4-aminoquinolines can be associated with several side effects, including gastrointestinal disturbances, pruritus, and, in rare cases, retinopathy. Long-term use, particularly of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine, requires monitoring for potential ocular toxicity.
Gallery[edit]
-
Chemical structure of Chloroquine
-
Chemical structure of Hydroxychloroquine