Methyl red: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
[[Category:Azo dyes]] | [[Category:Azo dyes]] | ||
{{chemistry-stub}} | {{chemistry-stub}} | ||
== Methyl_red == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Methyl_red.svg|Methyl red structure | |||
File:Methyl-red-from-xtal-3D-balls.png|Methyl red from crystal 3D balls | |||
File:Crystals_of_Methyl_red_sodium_salt.jpg|Crystals of Methyl red sodium salt | |||
File:Color_transition_of_Methyl_red_solution_under_different_acid-base_conditions.jpg|Color transition of Methyl red solution under different acid-base conditions | |||
File:Preparation_of_Methyl_Red.png|Preparation of Methyl Red | |||
File:Methyl_red_indicator.svg|Methyl red indicator | |||
File:Methylrot_Probe_methyl_red_test.jpg|Methyl red test | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 00:49, 27 February 2025
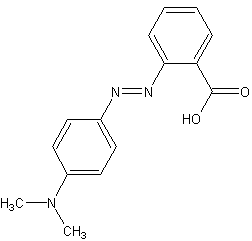
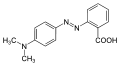
Methyl red (MR), also known as C.I. Acid Red 2, is an indicator dye that turns red in acidic solutions. It is a pH indicator used to identify the acidity of a solution. Methyl red is an azo dye, and it changes color at a pH of about 4.4 to 6.2, from red at pH 4.4 and below to yellow at pH 6.2 and above, with the transition range between these values appearing orange.
Chemistry[edit]
Methyl red is a chemical compound with the formula C15H15N3O2. It is part of the azo dye group, which are characterized by the presence of the functional group -N=N-, known as an azo group. In an acidic environment, methyl red offers a red color due to the presence of hydronium ions (H3O+) which stabilize the structure that absorbs at longer wavelengths. In neutral to basic conditions, the molecule exists in a form that absorbs at shorter wavelengths, thus appearing yellow.
Application[edit]
Methyl red is widely used in the laboratory as a pH indicator in titration experiments. It is particularly useful in acid-base titrations due to its clear and distinct color change. Besides its use in chemistry, methyl red is also employed in the microbiology field, specifically in the Methyl Red test, part of the IMViC tests, to identify bacteria that produce stable acid end products from glucose fermentation.
Methyl Red Test[edit]
The Methyl Red test is a procedure used in microbiology to detect the ability of microorganisms to perform mixed acids fermentation when supplied with glucose. The presence of acid end-products lowers the pH of the medium, and the addition of methyl red indicator to the culture turns the medium red, indicating a positive test. Organisms that utilize the butylene glycol pathway or other non-acidic pathways result in a negative test, with the medium turning yellow.
Safety[edit]
As with many azo dyes, there are safety considerations with methyl red. It should be handled with care in the laboratory, using appropriate personal protective equipment. Methyl red is considered to be a potential health hazard if ingested, inhaled, or comes into contact with skin and eyes.
Environmental Impact[edit]
The environmental impact of azo dyes, including methyl red, is a concern due to their synthetic nature and potential to release aromatic amines, some of which may be carcinogenic, upon degradation. Efforts are ongoing to develop more environmentally friendly alternatives and to improve the degradation processes of existing dyes to minimize their impact.
Methyl_red[edit]
-
Methyl red structure
-
Methyl red from crystal 3D balls
-
Crystals of Methyl red sodium salt
-
Color transition of Methyl red solution under different acid-base conditions
-
Preparation of Methyl Red
-
Methyl red indicator
-
Methyl red test