Morantel: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
[[Category:Anthelmintics]] | [[Category:Anthelmintics]] | ||
{{veterinary-medicine-stub}} | {{veterinary-medicine-stub}} | ||
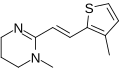
== Morantel == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Morantel.svg|Morantel | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 12:02, 25 February 2025
Morantel is an anthelmintic drug used primarily in the treatment of parasitic worm infections in animals. It belongs to the class of drugs known as tetrahydropyrimidines, which also includes pyrantel and oxantel. Morantel is not typically used in humans, but it is an important tool in veterinary medicine.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
Morantel works by acting on the neuromuscular junction of the parasitic worms. It causes a persistent activation of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on the worm's muscle cells, leading to paralysis and expulsion of the worm from the host organism.
Uses[edit]
Morantel is primarily used in the treatment of nematode infections in livestock, particularly sheep and goats. It is effective against a variety of nematodes, including those in the genera Haemonchus, Trichostrongylus, and Ostertagia.
Side Effects[edit]
As with any medication, morantel can cause side effects. In animals, these can include salivation, vomiting, and diarrhea. However, these side effects are generally rare and mild.
Resistance[edit]
Resistance to morantel and other tetrahydropyrimidines has been reported in some nematode populations. This is a significant concern in veterinary medicine, as it can limit the effectiveness of these drugs.
See Also[edit]

This veterinary medicine related article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it.
Morantel[edit]
-
Morantel