Agriculture in Nigeria: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
[[Category:Economy of Nigeria]] | [[Category:Economy of Nigeria]] | ||
[[Category:Agriculture by country]] | [[Category:Agriculture by country]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
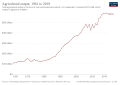
File:Agricultural_output_of_Nigeria.svg|Agricultural output of Nigeria | |||
File:Oshodi_market_lagos.jpg|Oshodi market Lagos | |||
File:Poultry_farm.jpg|Poultry farm | |||
File:Nigeria_econ_1979.jpg|Nigeria economy 1979 | |||
File:Ripe_Cocoa_Pods_Ready_for_Harvesting.jpg|Ripe Cocoa Pods Ready for Harvesting | |||
File:Latex_Extract_from_Rubber_Tree_in_Ogun_state.jpg|Latex Extract from Rubber Tree in Ogun state | |||
File:Palm_oil_in_a_white_bowl.jpg|Palm oil in a white bowl | |||
File:A_man_weeds_his_rice_crop.jpg|A man weeds his rice crop | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:40, 25 February 2025
Agriculture in Nigeria[edit]
Agriculture in Nigeria is a major sector of the economy, providing employment for a significant portion of the population and contributing to the country's GDP. Nigeria's diverse climate and geography allow for a variety of agricultural activities, ranging from crop production to livestock farming.
History[edit]
Agriculture has been a cornerstone of Nigeria's economy for centuries. Before the discovery of oil, agriculture was the mainstay of the Nigerian economy, with cash crops such as cocoa, groundnuts, palm oil, and cotton being major export products. The sector has undergone various transformations, especially during the colonial period and post-independence era, with efforts to modernize and increase productivity.
Major Crops[edit]
Nigeria is one of the largest producers of several agricultural products in Africa. Some of the major crops include:
- **Cassava**: Nigeria is the world's largest producer of cassava, a staple food for many Nigerians.
- **Yam**: The country is also a leading producer of yams, which are widely consumed across the nation.
- **Rice**: Rice is both a staple food and a cash crop, with efforts to increase local production to reduce import dependency.
- **Maize**: Maize is a crucial crop for both human consumption and animal feed.
- **Sorghum and Millet**: These are important cereals grown in the northern regions of Nigeria.
Livestock[edit]
Livestock farming is another vital component of Nigeria's agricultural sector. The country has a large population of cattle, goats, sheep, and poultry. Livestock provides meat, milk, and other products, contributing to food security and the economy.
Challenges[edit]
Despite its potential, the agricultural sector in Nigeria faces several challenges:
- **Infrastructure**: Poor infrastructure, such as roads and storage facilities, hampers the efficient distribution of agricultural products.
- **Access to Finance**: Many farmers lack access to credit facilities, limiting their ability to invest in modern farming techniques and equipment.
- **Climate Change**: Changes in weather patterns affect crop yields and livestock productivity.
- **Land Tenure System**: The land tenure system in Nigeria can be complex, affecting land availability and use.
Government Initiatives[edit]
The Nigerian government has implemented various policies and programs to boost agriculture, such as the Agricultural Transformation Agenda and the Green Alternative Policy. These initiatives aim to increase productivity, improve food security, and promote sustainable agricultural practices.
Also see[edit]
- Economy of Nigeria
- Food security in Nigeria
- Nigerian cuisine
- Cash crops in Nigeria
- Livestock farming in Nigeria
Template:Agriculture in Africa
-
Agricultural output of Nigeria
-
Oshodi market Lagos
-
Poultry farm
-
Nigeria economy 1979
-
Ripe Cocoa Pods Ready for Harvesting
-
Latex Extract from Rubber Tree in Ogun state
-
Palm oil in a white bowl
-
A man weeds his rice crop