Food loss and waste: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
Food loss and waste is a complex issue that requires collective action to mitigate its impacts. By implementing sustainable practices, improving infrastructure, educating consumers, and implementing supportive policies, we can work towards reducing food loss and waste, ensuring food security, and promoting a more sustainable future. | Food loss and waste is a complex issue that requires collective action to mitigate its impacts. By implementing sustainable practices, improving infrastructure, educating consumers, and implementing supportive policies, we can work towards reducing food loss and waste, ensuring food security, and promoting a more sustainable future. | ||
{{dictionary-stub1}} | {{dictionary-stub1}} | ||
== Food loss and waste == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Trashed_vegetables_in_Luxembourg.jpeg|Trashed vegetables in Luxembourg | |||
File:Food_Waste_Fiasco_(15819007150).jpg|Food Waste Fiasco | |||
File:A_RES_71_313_E.pdf|A RES 71 313 E | |||
File:A_conceptual_framework_for_Food_Loss_and_Waste_(FLW).svg|A conceptual framework for Food Loss and Waste (FLW) | |||
File:Protest_against_food_waste,_Berlin,_Germany.jpg|Protest against food waste, Berlin, Germany | |||
File:Food_Waste.jpg|Food Waste | |||
File:Food_Waste_Process.png|Food Waste Process | |||
File:Discarded_bagels.jpg|Discarded bagels | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:20, 25 February 2025
Food loss and waste is a significant global issue that has adverse social, economic, and environmental impacts. In this article, we will explore the causes, consequences, and potential solutions to address this problem.
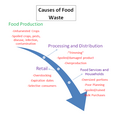
Causes of Food Loss and Waste[edit]
Food loss and waste can occur at various stages of the food supply chain. Some of the primary causes include:
Production[edit]
Agricultural practices such as improper harvesting techniques, inadequate storage facilities, and pest infestations can lead to significant food losses. Additionally, unpredictable weather conditions, natural disasters, and diseases can also contribute to crop failures and subsequent food waste.
Processing and Distribution[edit]
During the processing and distribution stages, food loss and waste can occur due to inefficient handling, packaging, and transportation practices. Lack of proper infrastructure, such as cold storage facilities and reliable transportation systems, can further exacerbate the problem.
Retail and Consumption[edit]
At the retail level, food loss and waste can result from overstocking, improper storage, and expiration of products. Consumer behavior, including excessive purchasing, improper food storage, and confusion over expiration dates, also contributes to food waste.
Consequences of Food Loss and Waste[edit]
The consequences of food loss and waste are far-reaching and impact various aspects of society and the environment.
Hunger and Food Insecurity[edit]
Food loss and waste deprive millions of people of access to nutritious food, exacerbating hunger and food insecurity. This is particularly concerning considering the increasing global population and the need to feed everyone adequately.
Economic Losses[edit]
Food loss and waste represent a significant economic loss for both producers and consumers. Farmers lose income due to crop spoilage, while consumers waste money on purchasing food that goes uneaten. Additionally, the costs associated with transportation, storage, and disposal of wasted food further strain the economy.
Environmental Impact[edit]
Food loss and waste have a substantial environmental impact. The resources used in food production, such as water, energy, and land, are wasted when food is discarded. Moreover, the decomposition of wasted food in landfills produces methane, a potent greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change.
Solutions to Address Food Loss and Waste[edit]
Addressing food loss and waste requires a multi-faceted approach involving various stakeholders, including governments, businesses, and consumers.
Improved Agricultural Practices[edit]
Implementing sustainable agricultural practices, such as efficient irrigation systems, integrated pest management, and post-harvest technologies, can help reduce food loss during production.
Enhanced Infrastructure and Logistics[edit]
Investing in infrastructure, such as cold storage facilities, reliable transportation systems, and efficient packaging, can minimize food loss and waste during processing and distribution.
Consumer Education[edit]
Raising awareness among consumers about the impacts of food waste and providing information on proper food storage, portion control, and expiration dates can help reduce waste at the retail and consumption levels.
Food Recovery and Redistribution[edit]
Establishing food recovery and redistribution programs can help redirect surplus food from retailers, restaurants, and households to those in need. This can be done through partnerships with food banks, charities, and community organizations.
Policy Interventions[edit]
Governments can play a crucial role in addressing food loss and waste by implementing policies and regulations that incentivize sustainable practices, promote food donation, and discourage wasteful behavior.
Conclusion[edit]
Food loss and waste is a complex issue that requires collective action to mitigate its impacts. By implementing sustainable practices, improving infrastructure, educating consumers, and implementing supportive policies, we can work towards reducing food loss and waste, ensuring food security, and promoting a more sustainable future.
Food loss and waste[edit]
-
Trashed vegetables in Luxembourg
-
Food Waste Fiasco
-
A RES 71 313 E
-
A conceptual framework for Food Loss and Waste (FLW)
-
Protest against food waste, Berlin, Germany
-
Food Waste
-
Food Waste Process
-
Discarded bagels