Befloxatone: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
== Befloxatone == | |||
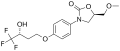
<gallery> | |||
File:Befloxatone_structure.svg|Befloxatone structure | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 23:50, 24 February 2025
Befloxatone is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) that was developed by Sanofi-Aventis for the treatment of depression. It acts by inhibiting the enzyme monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A), which breaks down serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine in the brain. By inhibiting this enzyme, befloxatone increases the levels of these neurotransmitters, which can help to alleviate the symptoms of depression.
History[edit]
Befloxatone was first synthesized in the 1990s by Sanofi-Aventis, a French multinational pharmaceutical company. It was developed as a potential treatment for depression, with the aim of providing a safer and more tolerable alternative to older MAOIs, which have significant side effects and dietary restrictions.
Pharmacology[edit]
Befloxatone is a selective and reversible inhibitor of MAO-A, an enzyme that degrades serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine in the brain. By inhibiting this enzyme, befloxatone increases the levels of these neurotransmitters, which can help to alleviate the symptoms of depression.
Clinical trials[edit]
Befloxatone has undergone several clinical trials to assess its efficacy and safety in the treatment of depression. However, the development of the drug was discontinued in the late 1990s due to concerns about its side effect profile.
Side effects[edit]
Like other MAOIs, befloxatone can cause a range of side effects, including nausea, dizziness, and insomnia. It can also cause a potentially dangerous increase in blood pressure if taken with certain foods or medications.