Optical illusion: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
[[Cognitive illusions]] are assumed to arise by interaction with assumptions about the world, leading to "unconscious inferences", an idea first suggested in the 19th century by the German physicist and physician [[Hermann von Helmholtz]]. | [[Cognitive illusions]] are assumed to arise by interaction with assumptions about the world, leading to "unconscious inferences", an idea first suggested in the 19th century by the German physicist and physician [[Hermann von Helmholtz]]. | ||
== Gallery == | |||
<gallery> | |||
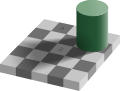
File:Checker_shadow_illusion.svg|Checker shadow illusion | |||
File:Grey_square_optical_illusion_proof2.svg|Grey square optical illusion proof | |||
File:Gregory_categorization_of_illusions_1991.png|Gregory categorization of illusions 1991 | |||
File:Mach_bands_-_animation.gif|Mach bands animation | |||
File:NeptunesGrottoOrganPlayer.jpg|Neptune's Grotto Organ Player | |||
File:Two_silhouette_profile_or_a_white_vase.svg|Two silhouette profile or a white vase | |||
File:Duck-Rabbit_illusion.jpg|Duck-Rabbit illusion | |||
File:Kanizsa_triangle.svg|Kanizsa triangle | |||
File:Vertical–horizontal_illusion.png|Vertical–horizontal illusion | |||
File:Ponzo_illusion.gif|Ponzo illusion | |||
File:Gradient-optical-illusion.svg|Gradient optical illusion | |||
</gallery> | |||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
* [[Visual perception]] | * [[Visual perception]] | ||
Latest revision as of 23:59, 23 February 2025
Optical illusion is a perception of visual stimuli that differs from reality. Optical illusions can be categorized into three main types: literal illusions, physiological illusions, and cognitive illusions.
Literal illusions[edit]
Literal illusions create images that are different from the objects that make them. These illusions are created by the physical properties of light, such as reflection, refraction, or interference.
Physiological illusions[edit]
Physiological illusions, such as the afterimage or moire pattern, are the effects on the eyes or brain of excessive stimulation of a specific type - brightness, color, size, position, tilt, movement, etc.
Cognitive illusions[edit]
Cognitive illusions are assumed to arise by interaction with assumptions about the world, leading to "unconscious inferences", an idea first suggested in the 19th century by the German physicist and physician Hermann von Helmholtz.
Gallery[edit]
-
Checker shadow illusion
-
Grey square optical illusion proof
-
Gregory categorization of illusions 1991
-
Mach bands animation
-
Neptune's Grotto Organ Player
-
Two silhouette profile or a white vase
-
Duck-Rabbit illusion
-
Kanizsa triangle
-
Vertical–horizontal illusion
-
Ponzo illusion
-
Gradient optical illusion
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />