West Indies: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Overview of the West Indies}} | |||
{{Use dmy dates|date=October 2023}} | |||
The '''West Indies''' is a region of the [[Caribbean]] that includes the island nations and territories located in the Caribbean Sea. This region is known for its diverse cultures, languages, and histories, as well as its significant role in global trade and tourism. | |||
The West Indies | |||
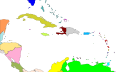
== | ==Geography== | ||
The West Indies | The West Indies consists of three main island groups: the [[Greater Antilles]], the [[Lesser Antilles]], and the [[Bahamas]]. These islands are situated in the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean, forming an arc from the tip of [[Florida]] to the northern coast of [[South America]]. | ||
== | ===Greater Antilles=== | ||
The | The Greater Antilles includes the larger islands of [[Cuba]], [[Hispaniola]] (shared by [[Haiti]] and the [[Dominican Republic]]), [[Jamaica]], and [[Puerto Rico]]. These islands are characterized by their mountainous terrain and rich biodiversity. | ||
== | ===Lesser Antilles=== | ||
[[ | The Lesser Antilles is a chain of smaller islands that extends from the Virgin Islands to Trinidad and Tobago. This group is further divided into the [[Leeward Islands]], the [[Windward Islands]], and the [[Leeward Antilles]]. | ||
== | ===Bahamas=== | ||
The | The Bahamas is an archipelago consisting of over 700 islands and cays, located to the north of Cuba and Hispaniola. The capital city is [[Nassau]], situated on the island of [[New Providence]]. | ||
== | ==History== | ||
The history of the West Indies is marked by the arrival of [[Christopher Columbus]] in 1492, which led to European colonization. The islands were originally inhabited by indigenous peoples such as the [[Arawak]] and [[Carib]]. | |||
===Colonial Era=== | |||
During the colonial era, the West Indies became a focal point for European powers, including [[Spain]], [[France]], [[Britain]], and the [[Netherlands]]. The region was heavily involved in the [[Atlantic slave trade]], which brought millions of enslaved Africans to work on sugar plantations. | |||
===Independence Movements=== | |||
In the 20th century, many West Indian territories gained independence from colonial rule. Notable independent nations include Jamaica (1962), Trinidad and Tobago (1962), and Barbados (1966). | |||
==Culture== | |||
The culture of the West Indies is a vibrant blend of African, European, and indigenous influences. This is reflected in the region's music, dance, cuisine, and festivals. | |||
===Music and Dance=== | |||
The West Indies is famous for its musical genres such as [[reggae]], [[soca]], [[calypso]], and [[dancehall]]. These styles have gained international popularity and are celebrated in festivals like [[Carnival]]. | |||
===Cuisine=== | |||
West Indian cuisine is known for its use of spices and tropical ingredients. Popular dishes include [[jerk chicken]], [[roti]], and [[ackee and saltfish]]. | |||
==Economy== | |||
The economy of the West Indies is diverse, with tourism, agriculture, and financial services playing significant roles. The region's natural beauty and warm climate make it a popular tourist destination. | |||
===Tourism=== | |||
Tourism is a major economic driver, with millions of visitors attracted to the beaches, resorts, and cultural heritage of the islands. | |||
===Agriculture=== | |||
Agriculture remains important, with products such as sugar, bananas, and coffee being key exports. | |||
==Related pages== | |||
* [[Caribbean Sea]] | |||
* [[Caribbean Community]] | * [[Caribbean Community]] | ||
* [[Caribbean | * [[Caribbean Basin Initiative]] | ||
[[Category:Caribbean]] | |||
[[Category:Regions of the Americas]] | [[Category:Regions of the Americas]] | ||
== West Indies == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Antillas_(orthographic_projection).svg|Antillas (orthographic projection) | |||
File:East_and_West_Indies.svg|East and West Indies | |||
File:West_Indies_-_Island_Groups.svg|West Indies - Island Groups | |||
File:Caribe-Político.svg|Caribe Político | |||
File:Atlantic-trench.JPG|Atlantic trench | |||
File:CIA_map_Central_America_&_Caribbean.png|CIA map Central America & Caribbean | |||
File:Life_expectancy_map_-Caribbean_-2019_-with_names.png|Life expectancy map - Caribbean - 2019 - with names | |||
File:Life_expectancy_map_-Caribbean_-2021_-with_names.png|Life expectancy map - Caribbean - 2021 - with names | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 21:17, 23 February 2025
Overview of the West Indies
The West Indies is a region of the Caribbean that includes the island nations and territories located in the Caribbean Sea. This region is known for its diverse cultures, languages, and histories, as well as its significant role in global trade and tourism.
Geography[edit]
The West Indies consists of three main island groups: the Greater Antilles, the Lesser Antilles, and the Bahamas. These islands are situated in the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean, forming an arc from the tip of Florida to the northern coast of South America.
Greater Antilles[edit]
The Greater Antilles includes the larger islands of Cuba, Hispaniola (shared by Haiti and the Dominican Republic), Jamaica, and Puerto Rico. These islands are characterized by their mountainous terrain and rich biodiversity.
Lesser Antilles[edit]
The Lesser Antilles is a chain of smaller islands that extends from the Virgin Islands to Trinidad and Tobago. This group is further divided into the Leeward Islands, the Windward Islands, and the Leeward Antilles.
Bahamas[edit]
The Bahamas is an archipelago consisting of over 700 islands and cays, located to the north of Cuba and Hispaniola. The capital city is Nassau, situated on the island of New Providence.
History[edit]
The history of the West Indies is marked by the arrival of Christopher Columbus in 1492, which led to European colonization. The islands were originally inhabited by indigenous peoples such as the Arawak and Carib.
Colonial Era[edit]
During the colonial era, the West Indies became a focal point for European powers, including Spain, France, Britain, and the Netherlands. The region was heavily involved in the Atlantic slave trade, which brought millions of enslaved Africans to work on sugar plantations.
Independence Movements[edit]
In the 20th century, many West Indian territories gained independence from colonial rule. Notable independent nations include Jamaica (1962), Trinidad and Tobago (1962), and Barbados (1966).
Culture[edit]
The culture of the West Indies is a vibrant blend of African, European, and indigenous influences. This is reflected in the region's music, dance, cuisine, and festivals.
Music and Dance[edit]
The West Indies is famous for its musical genres such as reggae, soca, calypso, and dancehall. These styles have gained international popularity and are celebrated in festivals like Carnival.
Cuisine[edit]
West Indian cuisine is known for its use of spices and tropical ingredients. Popular dishes include jerk chicken, roti, and ackee and saltfish.
Economy[edit]
The economy of the West Indies is diverse, with tourism, agriculture, and financial services playing significant roles. The region's natural beauty and warm climate make it a popular tourist destination.
Tourism[edit]
Tourism is a major economic driver, with millions of visitors attracted to the beaches, resorts, and cultural heritage of the islands.
Agriculture[edit]
Agriculture remains important, with products such as sugar, bananas, and coffee being key exports.
Related pages[edit]
West Indies[edit]
-
Antillas (orthographic projection)
-
East and West Indies
-
West Indies - Island Groups
-
Caribe Político
-
Atlantic trench
-
CIA map Central America & Caribbean
-
Life expectancy map - Caribbean - 2019 - with names
-
Life expectancy map - Caribbean - 2021 - with names