Hormonal intrauterine device: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|A type of long-acting reversible contraceptive device}} | |||
A '''hormonal intrauterine device''' (IUD) is a small, T-shaped plastic device that is inserted into the [[uterus]] to provide long-term [[contraception]]. It releases a hormone called [[levonorgestrel]], which is a type of [[progestin]]. This device is considered a form of [[long-acting reversible contraception]] (LARC) and is highly effective in preventing [[pregnancy]]. | |||
==Mechanism of Action== | ==Mechanism of Action== | ||
The hormonal IUD works by releasing levonorgestrel | The hormonal IUD works primarily by releasing levonorgestrel into the uterine cavity. This hormone thickens the [[cervical mucus]], making it difficult for [[sperm]] to enter the uterus and fertilize an [[egg]]. Additionally, levonorgestrel thins the [[endometrium]], reducing the likelihood of [[implantation]] should fertilization occur. In some cases, it may also inhibit [[ovulation]]. | ||
==Types== | ==Types of Hormonal IUDs== | ||
There are several types of hormonal IUDs available, varying in size, hormone dosage, and duration of effectiveness. Common brands include: | |||
* '''Mirena''': Effective for up to 7 years, releases 20 micrograms of levonorgestrel per day. | |||
* '''Kyleena''': Effective for up to 5 years, releases 17.5 micrograms of levonorgestrel per day. | |||
* '''Skyla''': Effective for up to 3 years, releases 14 micrograms of levonorgestrel per day. | |||
* '''Liletta''': Effective for up to 6 years, releases 19.5 micrograms of levonorgestrel per day. | |||
==Insertion and Removal== | |||
The insertion of a hormonal IUD is a procedure typically performed by a [[healthcare professional]]. It involves placing the device through the [[cervix]] into the uterus. The procedure can cause discomfort, but it is usually brief. Removal is also performed by a healthcare provider and involves gently pulling on the IUD strings to extract the device from the uterus. | |||
==Benefits== | ==Benefits== | ||
Hormonal IUDs offer several benefits, including: | |||
* High effectiveness in preventing pregnancy (over 99%). | |||
* Long-term protection, ranging from 3 to 7 years depending on the type. | |||
* Reduction in [[menstrual bleeding]] and [[dysmenorrhea]] (painful periods). | |||
* Rapid return to fertility upon removal. | |||
==Side Effects== | ==Side Effects== | ||
Some users may experience side effects, particularly in the first few months after insertion. These can include: | |||
* Irregular bleeding or spotting. | |||
* Headaches. | |||
* Breast tenderness. | |||
* Mood changes. | |||
* Ovarian cysts. | |||
==Contraindications== | ==Contraindications== | ||
Hormonal IUDs are not suitable for everyone. Contraindications include: | |||
* Current [[pelvic inflammatory disease]] (PID). | |||
* Known or suspected [[breast cancer]]. | |||
* Unexplained [[vaginal bleeding]]. | |||
* Severe [[liver disease]]. | |||
== | == Gallery == | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Mirena IntraUterine System.jpg|Hormonal intrauterine device | |||
File:Mirena IUD - Roe Becken ap.jpg|Hormonal intrauterine device | |||
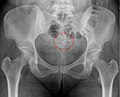
File:Mirena in optimal place - schematic.png|Hormonal intrauterine device | |||
File:Mirena in optimal place - ultrasound.jpg|Hormonal intrauterine device | |||
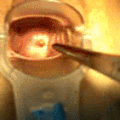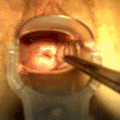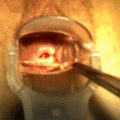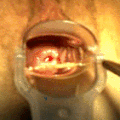
File:Mirena intrauterine device insertion.jpg|Hormonal intrauterine device | |||
File:Removal of IUD with progestogen.gif|Hormonal intrauterine device | |||
File:Mirena IUD with hand.jpg|Hormonal intrauterine device | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Related Pages== | |||
* [[Intrauterine device]] | |||
* [[Contraception]] | |||
* [[Levonorgestrel]] | |||
* [[Long-acting reversible contraception]] | |||
[[Category:Contraception]] | [[Category:Contraception]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Medical devices]] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:42, 21 February 2025
A type of long-acting reversible contraceptive device
A hormonal intrauterine device (IUD) is a small, T-shaped plastic device that is inserted into the uterus to provide long-term contraception. It releases a hormone called levonorgestrel, which is a type of progestin. This device is considered a form of long-acting reversible contraception (LARC) and is highly effective in preventing pregnancy.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
The hormonal IUD works primarily by releasing levonorgestrel into the uterine cavity. This hormone thickens the cervical mucus, making it difficult for sperm to enter the uterus and fertilize an egg. Additionally, levonorgestrel thins the endometrium, reducing the likelihood of implantation should fertilization occur. In some cases, it may also inhibit ovulation.
Types of Hormonal IUDs[edit]
There are several types of hormonal IUDs available, varying in size, hormone dosage, and duration of effectiveness. Common brands include:
- Mirena: Effective for up to 7 years, releases 20 micrograms of levonorgestrel per day.
- Kyleena: Effective for up to 5 years, releases 17.5 micrograms of levonorgestrel per day.
- Skyla: Effective for up to 3 years, releases 14 micrograms of levonorgestrel per day.
- Liletta: Effective for up to 6 years, releases 19.5 micrograms of levonorgestrel per day.
Insertion and Removal[edit]
The insertion of a hormonal IUD is a procedure typically performed by a healthcare professional. It involves placing the device through the cervix into the uterus. The procedure can cause discomfort, but it is usually brief. Removal is also performed by a healthcare provider and involves gently pulling on the IUD strings to extract the device from the uterus.
Benefits[edit]
Hormonal IUDs offer several benefits, including:
- High effectiveness in preventing pregnancy (over 99%).
- Long-term protection, ranging from 3 to 7 years depending on the type.
- Reduction in menstrual bleeding and dysmenorrhea (painful periods).
- Rapid return to fertility upon removal.
Side Effects[edit]
Some users may experience side effects, particularly in the first few months after insertion. These can include:
- Irregular bleeding or spotting.
- Headaches.
- Breast tenderness.
- Mood changes.
- Ovarian cysts.
Contraindications[edit]
Hormonal IUDs are not suitable for everyone. Contraindications include:
- Current pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
- Known or suspected breast cancer.
- Unexplained vaginal bleeding.
- Severe liver disease.
Gallery[edit]
-
Hormonal intrauterine device
-
Hormonal intrauterine device
-
Hormonal intrauterine device
-
Hormonal intrauterine device
-
Hormonal intrauterine device
-
Hormonal intrauterine device
-
Hormonal intrauterine device