Vine: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= Vine = | |||
[[File:Vine.jpg|thumb|right|A typical vine growing in a natural environment.]] | |||
A '''vine''' is any plant with a growth habit of trailing or [[climbing plant|climbing]] stems, [[liana|lianas]], or runners. The word "vine" can also refer to such stems or runners themselves, for instance, when used in [[viticulture]] (grape-growing) or [[horticulture]]. | |||
== Growth Habits == | |||
[[File:Helix_diagram-de.png|thumb|left|Diagram showing the helical growth pattern of vines.]] | |||
Vines | Vines can be divided into two broad categories: those that twine around a support and those that use tendrils or other structures to attach themselves to a support. Twining vines, such as [[morning glory]] and [[honeysuckle]], wrap their stems around a support. Tendril-bearing vines, such as [[grapevine]]s and [[passionflower]]s, use specialized structures to grip onto supports. | ||
Vines | == Types of Vines == | ||
== | === Climbing Vines === | ||
[[File:Schornstein_Kletterpflanze_Meidling.jpg|thumb|right|A climbing vine using a chimney as support.]] | |||
Climbing vines are plants that grow upwards by attaching themselves to a support structure. They can be found in many environments, from tropical rainforests to temperate woodlands. Some common climbing vines include [[ivy]], [[wisteria]], and [[clematis]]. | |||
== | === Twining Vines === | ||
Twining vines grow by wrapping their stems around a support. This type of growth is common in many species, including [[morning glory]] and [[honeysuckle]]. Twining vines can be either clockwise or counterclockwise in their growth pattern. | |||
=== Tendril-Bearing Vines === | |||
[[File:Brunnichia_ovata.jpg|thumb|left|Brunnichia ovata, a tendril-bearing vine.]] | |||
Tendril-bearing vines use specialized structures called tendrils to attach themselves to supports. These tendrils can be modified leaves, stems, or inflorescences. Examples of tendril-bearing vines include [[grapevine]]s and [[cucumber]]s. | |||
=== Lianas === | |||
Lianas are woody vines that are rooted in the ground and use trees as support to climb up to the canopy. They are a common feature of tropical rainforests and can be very large and heavy. Lianas include species such as [[rattan]] and [[Fockea edulis]]. | |||
[[File:Fockea_edulis_07_ies.jpg|thumb|right|Fockea edulis, a type of liana.]] | |||
== Ecological Role == | |||
Vines play a significant role in their ecosystems. They can provide food and habitat for a variety of animals, including birds, insects, and mammals. Vines can also affect the structure of the plant community by competing with trees and shrubs for light and nutrients. | |||
== Human Uses == | |||
Vines have been used by humans for various purposes throughout history. They are cultivated for their fruits, such as grapes and kiwifruit, and for ornamental purposes in gardens and landscapes. Some vines, like [[Momordica charantia]], are used in traditional medicine. | |||
== Related Pages == | |||
* [[Climbing plant]] | * [[Climbing plant]] | ||
* [[Liana]] | * [[Liana]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Viticulture]] | ||
* [[Horticulture]] | |||
[[Category: | [[Category:Plant morphology]] | ||
[[Category:Climbing plants]] | [[Category:Climbing plants]] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:15, 21 February 2025
Vine[edit]

A vine is any plant with a growth habit of trailing or climbing stems, lianas, or runners. The word "vine" can also refer to such stems or runners themselves, for instance, when used in viticulture (grape-growing) or horticulture.
Growth Habits[edit]
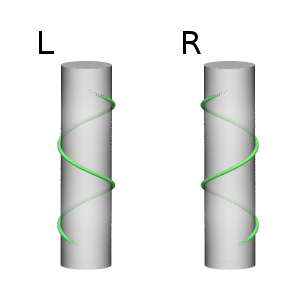
Vines can be divided into two broad categories: those that twine around a support and those that use tendrils or other structures to attach themselves to a support. Twining vines, such as morning glory and honeysuckle, wrap their stems around a support. Tendril-bearing vines, such as grapevines and passionflowers, use specialized structures to grip onto supports.
Types of Vines[edit]
Climbing Vines[edit]

Climbing vines are plants that grow upwards by attaching themselves to a support structure. They can be found in many environments, from tropical rainforests to temperate woodlands. Some common climbing vines include ivy, wisteria, and clematis.
Twining Vines[edit]
Twining vines grow by wrapping their stems around a support. This type of growth is common in many species, including morning glory and honeysuckle. Twining vines can be either clockwise or counterclockwise in their growth pattern.
Tendril-Bearing Vines[edit]

Tendril-bearing vines use specialized structures called tendrils to attach themselves to supports. These tendrils can be modified leaves, stems, or inflorescences. Examples of tendril-bearing vines include grapevines and cucumbers.
Lianas[edit]
Lianas are woody vines that are rooted in the ground and use trees as support to climb up to the canopy. They are a common feature of tropical rainforests and can be very large and heavy. Lianas include species such as rattan and Fockea edulis.

Ecological Role[edit]
Vines play a significant role in their ecosystems. They can provide food and habitat for a variety of animals, including birds, insects, and mammals. Vines can also affect the structure of the plant community by competing with trees and shrubs for light and nutrients.
Human Uses[edit]
Vines have been used by humans for various purposes throughout history. They are cultivated for their fruits, such as grapes and kiwifruit, and for ornamental purposes in gardens and landscapes. Some vines, like Momordica charantia, are used in traditional medicine.