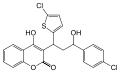
Tioclomarol: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|An anticoagulant medication}} | |||
{{Drugbox | |||
| verifiedfields = changed | |||
| verifiedrevid = 477002123 | |||
| image = Tioclomarol.svg | |||
| image_size = 200px | |||
}} | |||
'''Tioclomarol''' is an [[anticoagulant]] medication that is used to prevent the formation of harmful [[blood clots]] in the [[blood vessels]]. It is a [[coumarin]] derivative, similar to other anticoagulants such as [[warfarin]]. | |||
Tioclomarol | ==Mechanism of Action== | ||
Tioclomarol works by inhibiting the synthesis of [[vitamin K]]-dependent [[clotting factors]] in the [[liver]]. These clotting factors include [[factor II]], [[factor VII]], [[factor IX]], and [[factor X]]. By reducing the levels of these factors, tioclomarol decreases the blood's ability to clot, thus preventing thrombosis. | |||
== | ==Pharmacokinetics== | ||
Tioclomarol is administered orally and is absorbed through the [[gastrointestinal tract]]. It is metabolized in the liver and excreted primarily in the urine. The drug has a long half-life, which allows for once-daily dosing. | |||
==Clinical Use== | |||
Tioclomarol is used in the prevention and treatment of [[venous thromboembolism]], including [[deep vein thrombosis]] and [[pulmonary embolism]]. It is also used in patients with [[atrial fibrillation]] to reduce the risk of [[stroke]]. | |||
== | ==Side Effects== | ||
Common side effects of tioclomarol include [[bleeding]], [[bruising]], and [[gastrointestinal disturbances]]. Patients taking tioclomarol require regular monitoring of their [[International Normalized Ratio]] (INR) to ensure that their blood is not too thin. | |||
Tioclomarol is | ==Contraindications== | ||
Tioclomarol is contraindicated in patients with active bleeding, severe [[liver disease]], or [[hypersensitivity]] to the drug. It should be used with caution in patients with a history of [[peptic ulcer disease]] or [[hypertension]]. | |||
== | ==Interactions== | ||
Tioclomarol can interact with a variety of medications, including [[antibiotics]], [[antifungals]], and [[nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs]] (NSAIDs). These interactions can increase the risk of bleeding or reduce the effectiveness of tioclomarol. | |||
==Related pages== | |||
* [[Anticoagulant]] | |||
* [[Warfarin]] | |||
== | |||
* [[ | |||
* [[ | |||
* [[Vitamin K]] | * [[Vitamin K]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Thrombosis]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Anticoagulants]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Tioclomarol.svg|Tioclomarol | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:21, 20 February 2025
An anticoagulant medication
| Tioclomarol | |
|---|---|

| |
| INN | |
| Drug class | |
| Routes of administration | |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Bioavailability | |
| Metabolism | |
| Elimination half-life | |
| Excretion | |
| Legal status | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
Tioclomarol is an anticoagulant medication that is used to prevent the formation of harmful blood clots in the blood vessels. It is a coumarin derivative, similar to other anticoagulants such as warfarin.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
Tioclomarol works by inhibiting the synthesis of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors in the liver. These clotting factors include factor II, factor VII, factor IX, and factor X. By reducing the levels of these factors, tioclomarol decreases the blood's ability to clot, thus preventing thrombosis.
Pharmacokinetics[edit]
Tioclomarol is administered orally and is absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract. It is metabolized in the liver and excreted primarily in the urine. The drug has a long half-life, which allows for once-daily dosing.
Clinical Use[edit]
Tioclomarol is used in the prevention and treatment of venous thromboembolism, including deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. It is also used in patients with atrial fibrillation to reduce the risk of stroke.
Side Effects[edit]
Common side effects of tioclomarol include bleeding, bruising, and gastrointestinal disturbances. Patients taking tioclomarol require regular monitoring of their International Normalized Ratio (INR) to ensure that their blood is not too thin.
Contraindications[edit]
Tioclomarol is contraindicated in patients with active bleeding, severe liver disease, or hypersensitivity to the drug. It should be used with caution in patients with a history of peptic ulcer disease or hypertension.
Interactions[edit]
Tioclomarol can interact with a variety of medications, including antibiotics, antifungals, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). These interactions can increase the risk of bleeding or reduce the effectiveness of tioclomarol.
Related pages[edit]
-
Tioclomarol