Tricyclic: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Overview of tricyclic antidepressants}} | |||
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are a class of medications used | ==Tricyclic Antidepressants== | ||
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are a class of medications that are primarily used to treat [[depression]]. They are named for their chemical structure, which contains three rings of atoms. TCAs were first discovered in the 1950s and have been used extensively in the treatment of mood disorders. | |||
== | ==Mechanism of Action== | ||
TCAs work by inhibiting the reuptake of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, specifically [[norepinephrine]] and [[serotonin]]. By preventing the reabsorption of these neurotransmitters, TCAs increase their levels in the synaptic cleft, thereby enhancing neurotransmission and improving mood. | |||
== | ==Common Tricyclic Antidepressants== | ||
Some of the most commonly prescribed TCAs include: | |||
* [[Amitriptyline]] | * [[Amitriptyline]] | ||
* [[Nortriptyline]] | * [[Nortriptyline]] | ||
* [[Imipramine]] | |||
* [[Desipramine]] | * [[Desipramine]] | ||
* [[Clomipramine]] | |||
==Uses== | |||
While primarily used to treat depression, TCAs are also effective in treating a variety of other conditions, including: | |||
* [[Anxiety disorders]] | |||
* [[Chronic pain]] | |||
* [[Obsessive-compulsive disorder]] (OCD) | |||
* [[Panic disorder]] | |||
* [[Migraine]] prophylaxis | |||
== Related Pages == | ==Side Effects== | ||
TCAs are associated with a range of side effects due to their non-selective action on various neurotransmitter systems. Common side effects include: | |||
* [[Dry mouth]] | |||
* [[Constipation]] | |||
* [[Urinary retention]] | |||
* [[Blurred vision]] | |||
* [[Drowsiness]] | |||
More serious side effects can include [[cardiac arrhythmias]], particularly in overdose situations, and [[orthostatic hypotension]]. | |||
==Contraindications== | |||
TCAs should be used with caution in patients with certain medical conditions, such as: | |||
* [[Cardiovascular disease]] | |||
* [[Glaucoma]] | |||
* [[Prostatic hypertrophy]] | |||
==Comparison with Other Antidepressants== | |||
TCAs are often compared to other classes of antidepressants, such as [[selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors]] (SSRIs) and [[serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors]] (SNRIs). While TCAs are effective, they tend to have more side effects than these newer classes of medications, which has led to a decline in their use as first-line treatments. | |||
==History== | |||
The first TCA, [[imipramine]], was discovered in the late 1950s. It was initially developed as an antipsychotic but was found to have antidepressant properties. This discovery led to the development of other TCAs and their widespread use in the treatment of depression. | |||
==Related Pages== | |||
* [[Antidepressant]] | |||
* [[Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor]] | * [[Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor]] | ||
* [[Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor]] | |||
* [[Monoamine oxidase inhibitor]] | * [[Monoamine oxidase inhibitor]] | ||
[[Category:Antidepressants]] | |||
[[Category:Psychiatric drugs]] | |||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
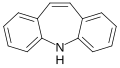
File:Dibenzazepine.svg|Dibenzazepine | File:Dibenzazepine.svg|Dibenzazepine | ||
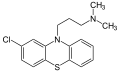
File:Phenothiazin.svg| | File:Phenothiazin.svg|Phenothiazin | ||
File:Imipramine.svg|Imipramine | File:Imipramine.svg|Imipramine | ||
File:Amitriptyline.svg|Amitriptyline | File:Amitriptyline.svg|Amitriptyline | ||
| Line 37: | Line 65: | ||
File:Tianeptine.svg|Tianeptine | File:Tianeptine.svg|Tianeptine | ||
File:Doxepin.svg|Doxepin | File:Doxepin.svg|Doxepin | ||
File:Chlorpromazin.svg| | File:Chlorpromazin.svg|Chlorpromazin | ||
File:Thioridazine.svg|Thioridazine | File:Thioridazine.svg|Thioridazine | ||
File: | File:Chlorprothixene structure.svg|Chlorprothixene | ||
File:Loxapine.svg|Loxapine | File:Loxapine.svg|Loxapine | ||
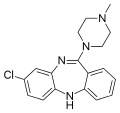
File:Clozapine.svg|Clozapine | File:Clozapine.svg|Clozapine | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 01:01, 20 February 2025
Overview of tricyclic antidepressants
Tricyclic Antidepressants[edit]
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are a class of medications that are primarily used to treat depression. They are named for their chemical structure, which contains three rings of atoms. TCAs were first discovered in the 1950s and have been used extensively in the treatment of mood disorders.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
TCAs work by inhibiting the reuptake of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, specifically norepinephrine and serotonin. By preventing the reabsorption of these neurotransmitters, TCAs increase their levels in the synaptic cleft, thereby enhancing neurotransmission and improving mood.
Common Tricyclic Antidepressants[edit]
Some of the most commonly prescribed TCAs include:
Uses[edit]
While primarily used to treat depression, TCAs are also effective in treating a variety of other conditions, including:
- Anxiety disorders
- Chronic pain
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
- Panic disorder
- Migraine prophylaxis
Side Effects[edit]
TCAs are associated with a range of side effects due to their non-selective action on various neurotransmitter systems. Common side effects include:
More serious side effects can include cardiac arrhythmias, particularly in overdose situations, and orthostatic hypotension.
Contraindications[edit]
TCAs should be used with caution in patients with certain medical conditions, such as:
Comparison with Other Antidepressants[edit]
TCAs are often compared to other classes of antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs). While TCAs are effective, they tend to have more side effects than these newer classes of medications, which has led to a decline in their use as first-line treatments.
History[edit]
The first TCA, imipramine, was discovered in the late 1950s. It was initially developed as an antipsychotic but was found to have antidepressant properties. This discovery led to the development of other TCAs and their widespread use in the treatment of depression.
Related Pages[edit]
- Antidepressant
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
- Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitor
-
Dibenzazepine
-
Phenothiazin
-
Imipramine
-
Amitriptyline
-
Iprindole
-
Tianeptine
-
Doxepin
-
Chlorpromazin
-
Thioridazine
-
Chlorprothixene
-
Loxapine
-
Clozapine