Ammonia poisoning: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
File:Aquarium_Nitrogen_Cycle.svg|Illustration of the nitrogen cycle in an aquarium | File:Aquarium_Nitrogen_Cycle.svg|Illustration of the nitrogen cycle in an aquarium | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
== Ammonia Poisoning == | |||
'''Ammonia poisoning''' occurs when a person is exposed to excessive amounts of ammonia, a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula NH_. Ammonia is a colorless gas with a characteristic pungent smell and is commonly found in household cleaners, industrial applications, and as a byproduct of agricultural activities. | |||
== Causes == | |||
Ammonia poisoning can result from inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact with ammonia. Common sources of exposure include: | |||
* [[Household cleaners]]: Many cleaning products contain ammonia, which can be harmful if inhaled or ingested. | |||
* [[Industrial exposure]]: Workers in industries such as agriculture, refrigeration, and chemical manufacturing may be exposed to ammonia. | |||
* [[Agricultural activities]]: Ammonia is used as a fertilizer and can be released into the air during its application. | |||
* [[Accidental release]]: Spills or leaks from storage tanks or transportation accidents can lead to high levels of ammonia in the environment. | |||
== Symptoms == | |||
The symptoms of ammonia poisoning vary depending on the route of exposure and the concentration of ammonia. Common symptoms include: | |||
* [[Respiratory distress]]: Coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing due to irritation of the respiratory tract. | |||
* [[Eye irritation]]: Redness, tearing, and burning sensation in the eyes. | |||
* [[Skin irritation]]: Redness, itching, and burns on the skin upon contact with liquid ammonia. | |||
* [[Gastrointestinal symptoms]]: Nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain if ammonia is ingested. | |||
* [[Neurological effects]]: Headache, dizziness, and confusion in severe cases. | |||
== Diagnosis == | |||
Diagnosis of ammonia poisoning is based on the patient's history of exposure and clinical symptoms. Medical professionals may perform the following: | |||
* [[Physical examination]]: To assess the extent of irritation and damage to the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract. | |||
* [[Blood tests]]: To measure ammonia levels in the blood and assess the severity of poisoning. | |||
* [[Pulmonary function tests]]: To evaluate respiratory function if inhalation exposure is suspected. | |||
== Treatment == | |||
Treatment for ammonia poisoning focuses on removing the source of exposure and providing supportive care: | |||
* [[Decontamination]]: Remove contaminated clothing and wash affected skin with water. | |||
* [[Oxygen therapy]]: Administer oxygen to patients with respiratory distress. | |||
* [[Bronchodilators]]: Use medications to relieve bronchospasm and improve breathing. | |||
* [[Intravenous fluids]]: Provide fluids to maintain hydration and support circulation. | |||
* [[Symptomatic treatment]]: Address specific symptoms such as pain or nausea. | |||
== Prevention == | |||
Preventing ammonia poisoning involves minimizing exposure and implementing safety measures: | |||
* [[Personal protective equipment]]: Use appropriate gear such as masks, gloves, and goggles when handling ammonia. | |||
* [[Ventilation]]: Ensure adequate ventilation in areas where ammonia is used or stored. | |||
* [[Training and education]]: Provide training for workers on the safe handling and storage of ammonia. | |||
* [[Emergency preparedness]]: Develop and practice emergency response plans for ammonia spills or leaks. | |||
== Related Pages == | |||
* [[Chemical poisoning]] | |||
* [[Occupational safety and health]] | |||
* [[Toxicology]] | |||
* [[Respiratory protection]] | |||
{{Toxicology}} | |||
{{Occupational safety}} | |||
[[Category:Poisoning]] | |||
[[Category:Toxicology]] | |||
[[Category:Occupational safety and health]] | |||
Latest revision as of 00:41, 19 February 2025
-
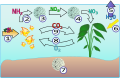
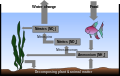
Diagram of the nitrogen cycle in an aquarium
-
Illustration of the nitrogen cycle in an aquarium
Ammonia Poisoning[edit]
Ammonia poisoning occurs when a person is exposed to excessive amounts of ammonia, a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula NH_. Ammonia is a colorless gas with a characteristic pungent smell and is commonly found in household cleaners, industrial applications, and as a byproduct of agricultural activities.
Causes[edit]
Ammonia poisoning can result from inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact with ammonia. Common sources of exposure include:
- Household cleaners: Many cleaning products contain ammonia, which can be harmful if inhaled or ingested.
- Industrial exposure: Workers in industries such as agriculture, refrigeration, and chemical manufacturing may be exposed to ammonia.
- Agricultural activities: Ammonia is used as a fertilizer and can be released into the air during its application.
- Accidental release: Spills or leaks from storage tanks or transportation accidents can lead to high levels of ammonia in the environment.
Symptoms[edit]
The symptoms of ammonia poisoning vary depending on the route of exposure and the concentration of ammonia. Common symptoms include:
- Respiratory distress: Coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing due to irritation of the respiratory tract.
- Eye irritation: Redness, tearing, and burning sensation in the eyes.
- Skin irritation: Redness, itching, and burns on the skin upon contact with liquid ammonia.
- Gastrointestinal symptoms: Nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain if ammonia is ingested.
- Neurological effects: Headache, dizziness, and confusion in severe cases.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of ammonia poisoning is based on the patient's history of exposure and clinical symptoms. Medical professionals may perform the following:
- Physical examination: To assess the extent of irritation and damage to the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract.
- Blood tests: To measure ammonia levels in the blood and assess the severity of poisoning.
- Pulmonary function tests: To evaluate respiratory function if inhalation exposure is suspected.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for ammonia poisoning focuses on removing the source of exposure and providing supportive care:
- Decontamination: Remove contaminated clothing and wash affected skin with water.
- Oxygen therapy: Administer oxygen to patients with respiratory distress.
- Bronchodilators: Use medications to relieve bronchospasm and improve breathing.
- Intravenous fluids: Provide fluids to maintain hydration and support circulation.
- Symptomatic treatment: Address specific symptoms such as pain or nausea.
Prevention[edit]
Preventing ammonia poisoning involves minimizing exposure and implementing safety measures:
- Personal protective equipment: Use appropriate gear such as masks, gloves, and goggles when handling ammonia.
- Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation in areas where ammonia is used or stored.
- Training and education: Provide training for workers on the safe handling and storage of ammonia.
- Emergency preparedness: Develop and practice emergency response plans for ammonia spills or leaks.
Related Pages[edit]
| Toxicology | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|