Eukaryote: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
[[Category:Eukaryotes]] | [[Category:Eukaryotes]] | ||
{{dictionary-stub1}} | {{dictionary-stub1}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Gram-negative_Bacteria_and_Paramecium_forming_cyst.jpg|Eukaryote | |||
File:California_Redwood_National_Park_(216450575).jpeg|Eukaryote | |||
File:Anim1754_-_Flickr_-_NOAA_Photo_Library_(rotated).jpg|Eukaryote | |||
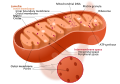
File:Mitochondrion_structure.svg|Eukaryote | |||
File:Chloroplast_II.svg|Eukaryote | |||
File:FluorescentCells.jpg|Eukaryote | |||
File:Sexual_cycle_N-2N.svg|Eukaryote | |||
File:Openly_available_illustrations_as_tools_to_describe_eukaryotic_microbial_diversity_-_Journal.pbio.3002395.g001.tif|Eukaryote | |||
File:Symbiogenesis_2_mergers.svg|Eukaryote | |||
File:Diskagma_butonii.jpg|Eukaryote | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 12:22, 18 February 2025
Eukaryote is a term in biology that refers to an organism whose cells contain a nucleus surrounded by a membrane, as well as other specialized organelles, all of which are enclosed by a plasma membrane. Eukaryotes include animals, plants, and fungi, but not bacteria or archaea.
Characteristics[edit]
Eukaryotic cells are typically much larger than those of prokaryotes. They have a variety of internal membrane-bound structures, called organelles, and a cytoskeleton composed of microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments, which play an important role in defining the cell's organization and shape.
Nucleus[edit]
The defining feature of eukaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear envelope, within which the cells' DNA is organized into structures called chromosomes. Each eukaryotic cell also contains other membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria and the Golgi apparatus.
Other Organelles[edit]
In addition to the nucleus, eukaryotic cells may contain several other types of organelles, which may include mitochondria, chloroplasts, the endoplasmic reticulum, the Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes. Each of these organelles performs a specific function critical for the cell to function properly.
Classification[edit]
Eukaryotes are classified into three main groups: Animalia, Plantae, and Fungi. Each of these groups is thought to be monophyletic, meaning that all organisms within each group are believed to have descended from a common ancestor.
Evolution[edit]
The origin and early evolution of eukaryotes is still not completely understood, but it is generally believed that they evolved from prokaryotic organisms through a process of endosymbiosis.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />