Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
{{Medicine-stub}} | {{Medicine-stub}} | ||
{{Radiology-stub}} | {{Radiology-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Myxoma_CMR.gif|Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging | |||
File:Coronal_localiser.jpg|Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging | |||
File:VLA.gif|Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging | |||
File:4-CH_cine_normal.gif|Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging | |||
File:LVSA.gif|Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging | |||
File:SAx_tag.gif|Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging | |||
File:4CH_IR_infarct.jpg|Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging | |||
File:4CH_cine_infarct.gif|Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging | |||
File:stress_moco.gif|Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging | |||
File:Cardiac_MRI_flow.gif|Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging | |||
File:Cardiac_MRI_streamlines.gif|Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging | |||
File:Cardiac_MRI_vector.gif|Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 12:19, 18 February 2025
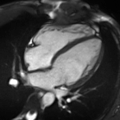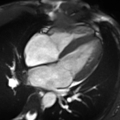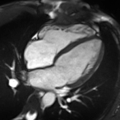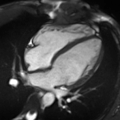
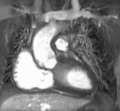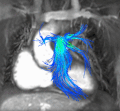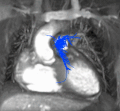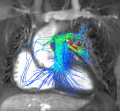
Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging (CMRI), also known as Cardiac MRI, is a medical imaging technology used primarily for the non-invasive assessment of the heart. It provides a detailed view of the heart's structure and function, aiding in the diagnosis and management of a wide range of heart conditions.
Overview[edit]
Cardiac MRI is a type of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) that specifically focuses on the heart and the surrounding blood vessels. It uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to create detailed images of the heart. Unlike other imaging techniques, such as Computed Tomography (CT) scans, MRI does not use ionizing radiation.
Applications[edit]
Cardiac MRI is used for a variety of clinical applications. It can assess the size and function of the heart chambers, evaluate the thickness and movement of the heart walls, and detect the presence of heart diseases such as coronary artery disease, cardiomyopathies, and congenital heart diseases. It can also identify areas of the heart that have been damaged by a heart attack, or assess the severity of heart valve problems.
Procedure[edit]
The procedure for a Cardiac MRI typically involves the patient lying on a table that slides into a large, tube-shaped machine. The patient is usually given a contrast agent to improve the visibility of certain tissues or blood vessels. The machine then uses a magnetic field and radio waves to create images of the heart. The procedure usually takes between 45 minutes to an hour.
Risks and Limitations[edit]
While Cardiac MRI is generally considered safe, there are some risks and limitations associated with the procedure. These include potential allergic reactions to the contrast agent, claustrophobia due to the enclosed space of the MRI machine, and the inability to use the procedure in patients with certain types of medical implants.
See Also[edit]
This radiology related article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it.
-
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging
-
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging
-
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging
-
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging
-
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging
-
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging
-
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging
-
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging
-
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging
-
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging
-
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging
-
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging