Working time: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
{{employment-stub}} | {{employment-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
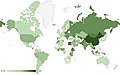
File:Average_annual_working_hours_per_employed_person,_OWID.svg|Average annual working hours per employed person | |||
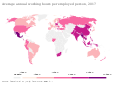
File:49時間以上労働者国際比較.png|International comparison of workers working more than 49 hours | |||
File:Weekly_Working_Hours_(Rescaled).jpg|Weekly working hours (rescaled) | |||
File:8hoursday_banner_1856.jpg|8-hour day banner 1856 | |||
File:1906_-_Grève_pour_les_8_heures.jpg|1906 - Strike for the 8-hour day | |||
File:US_work_week_-_GDP_-_GPI.jpg|US work week - GDP - GPI | |||
File:Annual_working_time_in_OECD.svg|Annual working time in OECD | |||
File:Nomorekaroshi-shimbashiprotest-june-13-2018.jpg|No more karoshi - Shimbashi protest June 13, 2018 | |||
File:US_working_hours_1950-2014.png|US working hours 1950-2014 | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 12:06, 18 February 2025
Working time is the period of time that a person spends at paid labor. Unpaid labor such as personal housework or caring for children or pets is not considered part of the working week. Many countries regulate the work week by law, such as stipulating minimum daily rest periods, annual holidays, and a maximum number of working hours per week. Working time may vary from person to person, often depending on economic conditions, location, culture, lifestyle choice, and the profitability of the individual's livelihood. For example, someone who is self-employed has the ability to tailor their working time to the needs of their personal lives, whereas someone who is employed by a company may have less flexibility.
History[edit]
The concept of working time has evolved dramatically over the centuries. In pre-industrial societies, there was a clear distinction between work time and non-work time. However, with the advent of the Industrial Revolution, this distinction became less clear as work was often performed at home. The introduction of the factory system in the 19th century further blurred the lines between work and non-work time, as workers were required to be at their jobs for set hours.
Regulation[edit]
Many countries have laws regulating the working time for employees. These laws often stipulate a maximum number of hours that an employee can work in a week, as well as rest periods and annual leave. The International Labour Organization has been instrumental in establishing international standards for working time, including the Forty-Hour Week Convention, 1935 and the Holidays with Pay Convention, 1936.
Health and safety[edit]
Working time is a significant factor in many health and safety issues. Long working hours can lead to stress, fatigue, and poor health. The World Health Organization has identified long working hours as a risk factor for certain health conditions, including cardiovascular disease.
See also[edit]
This employment related article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it.
-
Average annual working hours per employed person
-
International comparison of workers working more than 49 hours
-
Weekly working hours (rescaled)
-
8-hour day banner 1856
-
1906 - Strike for the 8-hour day
-
US work week - GDP - GPI
-
Annual working time in OECD
-
No more karoshi - Shimbashi protest June 13, 2018
-
US working hours 1950-2014