Nephron: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
{{dictionary-stub1}} | {{dictionary-stub1}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Kidney_Nephron.svg|Nephron | |||
File:Physiology_of_Nephron.png|Nephron | |||
File:Filtration_barrier.svg|Nephron | |||
File:2618_Nephron_Secretion_Reabsorption.jpg|Nephron | |||
File:Kidney_nephron_molar_transport_diagram.svg|Nephron | |||
File:Complex_proximal_tubule_with_acid_base.svg|Nephron | |||
File:Gray1133.png|Nephron | |||
File:Kidney_Nephron_Cells.png|Nephron | |||
File:Gray1129.png|Nephron | |||
File:Gray1130.svg|Nephron | |||
File:Kidney_tubules.png|Nephron | |||
File:Glomerular_Physiology.png|Nephron | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:43, 18 February 2025
Nephron
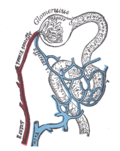
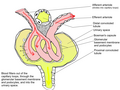
The nephron is the microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney. It is composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule. The renal corpuscle consists of a tuft of capillaries called a glomerulus and an encompassing Bowman's capsule. The renal tubule extends from the capsule.
Structure[edit]
The nephron is divided into two main parts: the renal corpuscle and the renal tubule.
Renal Corpuscle[edit]
The renal corpuscle is composed of two structures: the glomerulus and the Bowman's capsule. The glomerulus is a network of capillaries that performs the first step of filtering blood.
Renal Tubule[edit]
The renal tubule is a long, twisted tube that leads away from the glomerulus and into the kidney's medulla. It is divided into several sections, each with different cells and functions.
Function[edit]
The nephron carries out nearly all of the kidney's functions. Most notably, it filters blood and produces urine.
Filtration[edit]
Filtration is the process by which the kidneys filter out excess fluid and waste products from the bloodstream.
Reabsorption[edit]
Reabsorption is the process by which the kidneys return needed materials from the filtrate back into the bloodstream.
Secretion[edit]
Secretion is the process by which the kidneys remove additional wastes from the blood and add them to the filtrate.
Clinical significance[edit]
Damage to the nephrons can lead to kidney diseases such as chronic kidney disease and acute kidney injury. Treatment of these conditions depends on the cause and extent of the damage.