Cadmium: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
{{trace elements}} | {{trace elements}} | ||
{{stubd}} | {{stubd}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Cadmium_cutoff.png|Cadmium | |||
File:Friedrich_Stromeyer.jpg|Friedrich Stromeyer | |||
File:CadmiumMetalUSGOV.jpg|Cadmium metal | |||
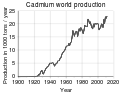
File:Cadmium_-_world_production_trend.svg|World production trend of cadmium | |||
File:2022cadmium.png|Cadmium | |||
File:NiCd_various.jpg|Nickel-cadmium batteries | |||
File:CdSeqdots.jpg|Cadmium selenide quantum dots | |||
File:Tyne_and_Wear_Metro_train_4001_at_Pelaw_01.jpg|Tyne and Wear Metro train | |||
File:Cadmium_sulfide.jpg|Cadmium sulfide | |||
File:HeCd_laser.jpg|Helium-cadmium laser | |||
File:Jinzu_River.jpg|Jinzu River | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:23, 18 February 2025
(KAD-mee-um) A metallic element that occurs naturally in tiny amounts in air, water, soil, and food. It is a byproduct of zinc refining and is used to make batteries, pigments, plastics, alloys, and electroplate. It is also found in tobacco and tobacco smoke. Exposure to high levels of cadmium may cause certain cancers and other health problems.
Information about Cadmium[edit]
Cadmium is a trace element and transitional metal that is not believed to play a role in higher biologic systems or in human nutrition.
Deficiency of Cadmium[edit]
Cadmium deficiency has not been convincingly shown in humans. Cadmium is toxic in moderate doses and is a potent antagonist of several essential minerals including calcium, iron, copper and zinc. Cadmium is used in the manufacture of batteries, electrical conductors and metal plating. Cadmium is also a byproduct of the mining and processing of iron, nickel and other metals and can be toxic to welders and industrial workers, producing a syndrome due to inhalation of excessive amounts known as cadmium fume fever.
Cadmium poisoning[edit]
Environmental exposure to excess cadmium has been reported due to contamination of the water supply from mining or manufacturing with subsequent concentration of cadmium in agricultural products such as rice, resulting in outbreaks of cadmium poisoning. A disease marked by bone fractures (itai-ita or "ouch-ouch" disease) arose after World War II in a rural area of Japan and was later linked to cadmium contamination of water used to irrigate rice fields. Itai-itai is characterized by renal tubular abnormalities and calcium and phosphate wasting resulting in osteomalacia. Chronic cadmium exposure has been linked to pulmonary fibrosis, chronic renal injury and an increased risk of cancer.
Liver safety of Cadmium[edit]
Cadmium has not been linked specifically to clinically apparent liver injury in humans although it, like many metals, is toxic to hepatocytes in vitro and causes acute liver injury in experimental animals. Autopsy material from patients with itai-itai disease demonstrates slight increase in fibrosis and steatosis, but the clinical manifestations appear minimal despite high levels of cadmium in liver tissue. The relative lack of hepatic injury with chronic cadmium exposure may relate to potent metallothionein induction in the liver by the trace metal. Cadmium in small quantities is included in many homeopathic medications and in several over-the-counter dietary supplements used to increase vitality and wellness.
Trace Elements in Tissues and Biologic Systems[edit]
| Aluminum | Copper | Nickel |
| Antimony | Fluorine | Rubidium |
| Barium | Iodine | Selenium |
| Boron | Lead | Silver |
| Bromine | Lithium | Strontium |
| Cadmium | Manganese | Tin |
| Chromium | Mercury | Vanadium |
| Cobalt | Molybdenum | Zinc |
-
Cadmium
-
Friedrich Stromeyer
-
Cadmium metal
-
World production trend of cadmium
-
Cadmium
-
Nickel-cadmium batteries
-
Cadmium selenide quantum dots
-
Tyne and Wear Metro train
-
Cadmium sulfide
-
Helium-cadmium laser
-
Jinzu River