Dorsal root of spinal nerve: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
[[Category:Neuroanatomy]] | [[Category:Neuroanatomy]] | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
== Dorsal_root_of_spinal_nerve == | |||
<gallery> | |||
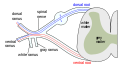
File:spinal_nerve.svg|Diagram of a spinal nerve | |||
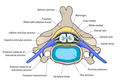
File:Cervical_vertebra_english.png|Cervical vertebra | |||
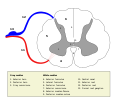
File:Medulla_spinalis_-_Section_-_English.svg|Cross-section of the spinal cord | |||
File:Gray675.png|Diagram of the spinal cord and spinal nerves | |||
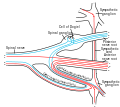
File:Gray759.png|Spinal nerve roots | |||
File:Gray770-en.svg|Spinal cord and nerve roots | |||
File:Gray796.png|Spinal nerve and vertebra | |||
File:Gray799.svg|Spinal nerve anatomy | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:16, 18 February 2025
Dorsal Root of Spinal Nerve
The dorsal root of the spinal nerve, also known as the posterior root, is a critical component of the nervous system. It is one of two nerve roots that emerge from the spinal cord, the other being the anterior (ventral) root. The dorsal root is responsible for transmitting sensory information from the periphery to the central nervous system (CNS), playing a pivotal role in the sensation process.
Anatomy[edit]
The dorsal root consists of sensory nerve fibers that originate from sensory neurons located within the dorsal root ganglion. This ganglion is a cluster of nerve cell bodies (neurons) situated just outside the spinal cord. Each spinal nerve is formed by the union of a dorsal and a ventral root, with the dorsal root carrying sensory information and the ventral root carrying motor information. The point where they merge is known as the spinal nerve proper, which then branches out to various parts of the body.
Function[edit]
The primary function of the dorsal root is to convey sensory information from the sensory receptors in the body to the spinal cord. This information can include touch, pain, temperature, and proprioception (the sense of body position). Once the sensory information reaches the spinal cord via the dorsal root, it can be processed and relayed to the brain for further interpretation.
Clinical Significance[edit]
Damage or disease affecting the dorsal root can lead to sensory deficits or neuropathic pain. Conditions such as radiculopathy (nerve root disease) and herpes zoster (shingles), which can affect the dorsal root ganglia, may result in significant discomfort and neurological symptoms. Diagnosis of dorsal root disorders typically involves neuroimaging techniques, such as MRI, and nerve conduction studies.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for conditions affecting the dorsal root depends on the underlying cause. It may include medications for pain relief, physical therapy to maintain or improve function, and in some cases, surgical intervention to relieve pressure on the nerve root.
Research Directions[edit]
Ongoing research in the field of neurology and neurosurgery continues to explore better ways to treat and manage conditions affecting the dorsal root. This includes the development of novel pharmacological treatments, improvements in surgical techniques, and the use of stem cell therapy and neuroprosthetics for nerve repair and regeneration.
Dorsal_root_of_spinal_nerve[edit]
-
Diagram of a spinal nerve
-
Cervical vertebra
-
Cross-section of the spinal cord
-
Diagram of the spinal cord and spinal nerves
-
Spinal nerve roots
-
Spinal cord and nerve roots
-
Spinal nerve and vertebra
-
Spinal nerve anatomy