Zinc finger: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Zinc_finger_rendered.png|Zinc finger rendered | |||
File:Zinc_finger_DNA_complex.png|Zinc finger DNA complex | |||
File:PDB_1zaa_EBI.jpg|Zinc finger | |||
File:PDB_1ncp_EBI.jpg|Zinc finger | |||
File:PDB_1pft_EBI.jpg|Zinc finger | |||
File:PDB_1d66_EBI.jpg|Zinc finger | |||
File:PDB_1pxe_EBI.jpg|Zinc finger | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:09, 18 February 2025
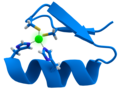
Zinc finger is a small protein structure that is characterized by the coordination of one or more zinc ions in order to stabilize the fold. Originally coined to describe the finger-like appearance of a hypothesized structure from X-ray diffraction, the term now refers to a wide variety of differing protein structures.
Structure[edit]
Zinc fingers form parts of some transcription factors, which are proteins that recognize DNA sequences. They do this by creating a binding site where the zinc ion and the amino acids from the zinc finger protein interact with the DNA molecule. This interaction allows the transcription factor to bind to the DNA sequence and regulate the transcription of DNA to mRNA.
Types[edit]
There are many types of zinc fingers. The classical zinc finger, also known as the Cys2His2 (C2H2) zinc finger, is the most commonly found type in the human genome. Other types include the Cys4, Cys6, and Cys2HisCys zinc fingers. Each type has a unique structure and function.
Function[edit]
Zinc fingers play crucial roles in various biological processes. They are involved in gene regulation, DNA repair, lipid binding, and protein folding. They can also act as enzymes, performing reactions that involve the transfer of functional groups to other molecules.
Clinical significance[edit]
Mutations in zinc finger proteins have been associated with a number of diseases, including some types of cancer, autoimmune diseases, and neurodegenerative diseases. Understanding the structure and function of zinc fingers can therefore provide important insights into the mechanisms of these diseases.