Ileum: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Illu_small_intestine.jpg|Diagram of the small intestine | |||
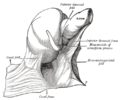
File:Gray1045.png|Gray's Anatomy illustration of the ileum | |||
File:Gut_wall.svg|Diagram of the gut wall | |||
File:Gobletcell.jpg|Goblet cell in the ileum | |||
File:Peyer's_patch_(improved_color).jpg|Peyer's patch in the ileum | |||
File:Cross-section_histology_of_small_intestinal_villi_of_the_terminal_ileum.jpg|Histology of ileum villi | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 10:58, 18 February 2025
Ileum is the final section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In humans, the ileum is about 2–4 m long, and follows the duodenum and jejunum, and is separated from the cecum by the ileocecal valve (ICV).
Anatomy[edit]
The ileum follows the duodenum and jejunum and is separated from the cecum by the ileocecal valve. In humans, the ileum is about 2–4 m long, and it is usually narrower and thinner-walled than the jejunum. It has a smaller caliber with less vascular arborization and less active transport than the jejunum.
Function[edit]
The main function of the ileum is to absorb vitamin B12, bile salts, and whatever products of digestion were not absorbed by the jejunum. The wall itself is made up of folds, each of which has many tiny finger-like projections known as villi, on its surface. In turn, the epithelial cells which line these villi possess even larger numbers of microvilli. Therefore, the ileum has an extremely large surface area both for the adsorption (attachment) of enzyme molecules and for the absorption of products of digestion.
Clinical significance[edit]
Diseases of the ileum can result in a number of medical conditions, including Crohn's disease and ileitis. These conditions can lead to various symptoms, including abdominal pain, weight loss, and diarrhea. Treatment options vary depending on the specific condition and its severity, but may include dietary changes, medication, or surgery.