Cotyledon: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
[[Category:Plant reproduction]] | [[Category:Plant reproduction]] | ||
[[Category:Leaves]] | [[Category:Leaves]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Cotyledon-Cercis_siliquastrum.jpg|Cercis siliquastrum cotyledon | |||
File:Monocot_vs_dicot_crop_Pengo.jpg|Monocot vs dicot comparison | |||
File:Germination-en.svg|Germination process | |||
File:Peanut_cotyledons.jpg|Peanut cotyledons | |||
File:09-05-31_Abeto_Douglas.jpg|Douglas fir cotyledon | |||
File:Mimosa_pudica_-_cotyledon.jpg|Mimosa pudica cotyledon | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 10:58, 18 February 2025
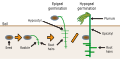
A cotyledon is a fundamental part of a plant embryo found within a seed. It is commonly referred to as the "seed leaf" and derives its name from the Latin word "cotyledon". Botanists use the number of cotyledons present to classify angiosperms, or flowering plants. Monocots, which have one cotyledon, and dicots, which have two cotyledons, are the two main types of flowering plants.
In dicotyledonous seedlings, the cotyledons serve as embryonic leaves and function similarly to true leaves. However, the two are developmentally distinct, with cotyledons forming during embryogenesis along with the root and shoot meristems before germination. True leaves, on the other hand, form post-embryonically from the shoot apical meristem after germination.
The cotyledons of monocots, including grasses, are highly modified leaves composed of a scutellum and a coleoptile. The scutellum absorbs stored food from the adjacent endosperm, and the coleoptile covers the plumule, which is the precursor to the stem and leaves of the plant.
Gymnosperm seedlings also have cotyledons, with the number varying across species. Gnetophytes, cycads, and ginkgos all have two cotyledons, while conifers have variable numbers, with some species having up to 24. Cotyledons can be ephemeral, lasting only a few days after emergence, or persistent, lasting at least a year on the plant. They contain stored food reserves from the seed, which are used up as the seedling grows.
Other uses of the term[edit]
- 1. Any one of the enlarged, vascular villi of the chorion which project into depressions of the decidua vera.
- 2. Any one of the numerous rounded portions into which the uterine surface of the placenta is divided.
- 3. A genus of plants of the order Crassulacece. C. umbilicus, navelwort of Europe, has been highly recommended in epilepsy, but its medicinal properties are feeble.