Oncovirus: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
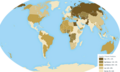
File:PrevalenceHepB2014.png|Prevalence of Hepatitis B in 2014 | |||
File:Viral_Tegument.svg|Diagram of Viral Tegument | |||
File:Oncogenes_illustration.jpg|Illustration of Oncogenes | |||
File:Anaplastic_astrocytoma_-_p53_-_very_high_mag.jpg|Anaplastic Astrocytoma with p53 staining | |||
File:Kaposis_sarcoma_01.jpg|Kaposi's Sarcoma | |||
File:2r5k.jpg|Structure of a viral protein | |||
File:HBV.png|Hepatitis B Virus | |||
File:Rabbit_shopes_papilloma_virus_3.jpg|Rabbit Shope's Papilloma Virus | |||
File:15_Hegasy_Nobel_Prize_2020_HepC.jpg|Nobel Prize 2020 for Hepatitis C | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 10:54, 18 February 2025
Oncovirus is a type of virus that can cause cancer. This property is not universal to all viruses but is limited to a select few in a specific subset. Oncoviruses are categorized as DNA or RNA viruses. The DNA oncoviruses include the human papillomavirus, Epstein-Barr virus, Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV), and the hepatitis B virus. The RNA oncoviruses include HTLV-1 and the hepatitis C virus.
Types of Oncoviruses[edit]
DNA Oncoviruses[edit]
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV) - Certain types of HPV are known to cause cervical cancer, anal cancer, oropharyngeal cancer, vulvar cancer, vaginal cancer, and penile cancer.
- Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) - EBV is associated with various types of conditions including Burkitt's lymphoma, Hodgkin's lymphoma, gastric cancer, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, and conditions associated with HIV/AIDS.
- Kaposi's Sarcoma-associated Herpesvirus (KSHV) - KSHV is associated with Kaposi's sarcoma, primary effusion lymphoma, and some types of multicentric Castleman's disease.
- Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) - Chronic infection with HBV can lead to liver cirrhosis or cancer.
RNA Oncoviruses[edit]
- Human T-lymphotropic Virus (HTLV-1) - HTLV-1 is known to cause adult T-cell leukemia and lymphoma.
- Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) - Chronic infection with HCV can lead to liver cirrhosis or cancer.
Mechanism of Oncoviruses[edit]
Oncoviruses can cause cancer by integrating their genetic material into the host cell's DNA. This can disrupt normal cell function, leading to uncontrolled cell growth and division, which can result in the formation of a tumor.
Prevention and Treatment[edit]
Prevention of oncovirus infection can be achieved through vaccination (for HPV and HBV), safe sex practices (for HPV, HBV, and HCV), and regular screening for at-risk populations. Treatment options for oncovirus-associated cancers include antiviral therapy, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and surgery.
|
|
|
-
Prevalence of Hepatitis B in 2014
-
Diagram of Viral Tegument
-
Illustration of Oncogenes
-
Anaplastic Astrocytoma with p53 staining
-
Kaposi's Sarcoma
-
Structure of a viral protein
-
Hepatitis B Virus
-
Rabbit Shope's Papilloma Virus
-
Nobel Prize 2020 for Hepatitis C