Natural resource economics: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
{{Economics-stub}} | {{Economics-stub}} | ||
{{Environment-stub}} | {{Environment-stub}} | ||
== Natural_resource_economics == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Nested_sustainability-v2.gif|Nested sustainability model | |||
File:Nitrogen_Cycle.jpg|Diagram of the nitrogen cycle | |||
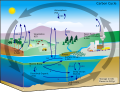
File:Water_cycle.png|Illustration of the water cycle | |||
File:Carbon_cycle-cute_diagram.svg|Diagram of the carbon cycle | |||
File:Oxygen_Cycle.jpg|Diagram of the oxygen cycle | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 05:01, 18 February 2025
Natural resource economics is a branch of economics that deals with the supply, demand, and allocation of the Earth's natural resources. It is an interdisciplinary field of academic research that combines aspects of environmental economics, ecology, and sustainable development.
Overview[edit]
Natural resource economics focuses on the demand, supply, and allocation of natural resources in an economic system. It aims to understand the role of natural resources in the economy in order to develop more sustainable methods of managing those resources. It takes into account the fact that natural resources are finite and can be exhausted if not managed properly.
History[edit]
The field of natural resource economics has its roots in the work of classical economists such as Adam Smith and David Ricardo, who considered natural resources as one of the three factors of production, along with labor and capital. However, it was not until the 20th century that natural resource economics emerged as a distinct field of study, largely in response to concerns about resource depletion and environmental degradation.
Key Concepts[edit]
Resource Scarcity[edit]
One of the key concepts in natural resource economics is resource scarcity. This refers to the limited availability of natural resources, which can lead to competition and conflict over their use.
Resource Allocation[edit]
Another important concept is resource allocation, which involves deciding how to distribute resources among different uses. This is often a complex process that involves trade-offs between economic efficiency and environmental sustainability.
Sustainable Development[edit]
Sustainable development is a central goal of natural resource economics. This involves managing resources in a way that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>

This article is a environment-related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Natural_resource_economics[edit]
-
Nested sustainability model
-
Diagram of the nitrogen cycle
-
Illustration of the water cycle
-
Diagram of the carbon cycle
-
Diagram of the oxygen cycle