Malonic acid: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
{{Chemistry-stub}} | {{Chemistry-stub}} | ||
== Malonic_acid == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Malonsäure.svg|Malonic acid structure | |||
File:Synthesis_of_malonic_acid.png|Synthesis of malonic acid | |||
File:KnoevenagelGeneral.png|Knoevenagel condensation | |||
File:Doebner_modification.png|Doebner modification | |||
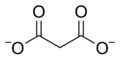
File:Malonate.png|Malonate ion | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:59, 18 February 2025
Malonic acid (IUPAC name: propanedioic acid) is a dicarboxylic acid with the chemical formula C3H4O4. Its structural formula is CH2(COOH)2. Malonic acid is a colorless, crystalline substance that is soluble in water and can be derived from the oxidation of malic acid found in apples and is also present in grapes, watermelons, and beetroot. It plays a significant role in various biochemical processes and is a key intermediate in the Krebs cycle, which is vital for energy production in cellular respiration.
Properties and Synthesis[edit]
Malonic acid is known for its high solubility in water and its ability to form metal salts, known as malonates, which are often used in various industrial applications. The acid itself is produced industrially through the hydrolysis of cyanoacetic acid with sulfuric acid, a process that yields high purity malonic acid. It can also be synthesized through the carbonation of sodium chloroacetate with sodium carbonate.
Applications[edit]
Malonic acid and its derivatives, particularly diethyl malonate, are used in a wide range of chemical syntheses, including the production of barbiturates, vitamin B1, and flavorings. Its ability to undergo nucleophilic substitution makes it a valuable building block in the synthesis of more complex organic compounds. Malonic acid is also employed in the Malonic ester synthesis, a method for preparing carboxylic acids.
In addition to its industrial uses, malonic acid has potential applications in medicine and pharmacology. It has been studied for its inhibitory effects on certain enzymes, which could lead to therapeutic applications in treating diseases where these enzymes are implicated.
Health and Safety[edit]
While malonic acid is generally considered safe, it can be irritating to the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract upon exposure. Handling of malonic acid should be done with appropriate safety precautions, including the use of personal protective equipment. Ingestion of large amounts can be harmful, and appropriate measures should be taken to prevent accidental ingestion.
Environmental Impact[edit]
Malonic acid is biodegradable and is not considered a major environmental hazard. However, its production and use in industrial processes must be managed to minimize any potential environmental impacts, including proper waste management and treatment practices.
See Also[edit]
Malonic_acid[edit]
-
Malonic acid structure
-
Synthesis of malonic acid
-
Knoevenagel condensation
-
Doebner modification
-
Malonate ion